When customer requests come from every direction—email, phone, chat, or social media—without a proper ticketing system, it quickly turns into chaos. Challenges pile up, responses are delayed, and things start to spin out of control. But with effective customer service ticketing software in place, every request is tracked, prioritized, and resolved efficiently.
With 73% of customers ready to leave after a single bad experience, meeting customer expectations is critical (TCN Consumer Survey). A good ticketing system is a must-have; it keeps your team organized, responds faster, ensures that no issue goes unresolved, and, last but not least, keeps customers satisfied and loyal.
In this article, we'll discuss how customer support ticketing systems work, the benefits they bring, and the features to focus on. We will also provide step-by-step guides on choosing the right one and review five of the best ticketing systems on the market.
What is a ticketing system?
A ticketing system is a centralized platform for managing customer support requests. When a customer faces a problem or has a query, creating a ticket is the first step toward a timely resolution. It collects all the necessary customer details about the issue, making it easier for the support team to handle it quickly and effectively.
What are the different types of ticketing systems?
Each company has its specific requirements, leading to a variety of ticketing tool options that cater to different criteria across industries. The purpose of use can differ: some focus on handling incoming requests, others on monitoring software bugs, and some provide internal support.
Let's review the following types, which help businesses achieve their specific goals and deliver excellent service:
- Help desk ticketing software focuses on managing customer queries and providing internal support. They typically include omnichannel support, automated workflows, ticket routing, and analytics to track performance.
- Customer service desk solutions are a traditional example of a ticketing system. It aims to manage customer support requests across multiple channels. Key features include ticket management, automated workflows, reporting tools, and knowledge bases for self-service solutions.
- IT help desk systems represent the central hub for managing incidents and support requests within an organization, serving as a centralized repository for all technical issues. It intends to solve various technical difficulties, from hardware to network issues.
- Issue-tracking solutions address the challenges related to software development in one place (e.g., reported bugs, errors in software code, and other issues). It helps log and prioritize issues and monitor their progress until resolved.
How does a ticketing system work?
Ticket systems collect all requests in one place, ensuring no essential information is lost. Customer service ticketing software helps support reps easily track the status of each customer request, identify the assigned agent, and access a comprehensive history of all previous interactions.
Ultimately, implementing a ticketing tool simplifies customer service operations and makes your customer experience more pleasant.
Key benefits of implementing a ticketing system
Let’s be honest, help desks don’t come cheap. And they take time and resources to maintain. (Read how the on-premise vs cloud help desks differ for more details on that topic.) But you’ll understand why they’re worth the investment once you’ve considered the following benefits of ticketing systems:
#1 Improved organization and efficiency
Ticketing systems come with automated features that streamline the entire customer service process. From support ticket routing to data analytics, you’ll get the tools you need to maintain smooth and cost-effective support operations.
#2 Better tracking and accountability of support tasks
Help desks allow your teams to manage all the tickets in a centralized system. You’ll see who’s assigned to the customer and how far along they are in the resolution process. You’ll know who’s accountable if mistakes are made or if issues aren’t resolved.
#3 Data-driven insights for continuous improvement
Customer service ticketing systems enable you to track resolution time, transfer rate, net promotion score (NPS), and other KPIs. Keeping tabs on the performance of your agents and the satisfaction levels of your customers will help you identify areas for improvement and make any necessary changes.
#4 Streamlined communication between support teams and customers
Help desks allow agents to view all interactions from a single location. Even if your customers switch between channels, your customer service reps can still continue the conversations without a hitch. Your clients won’t have to repeat themselves over and over.
#5 Ability to prioritize and categorize issues effectively
Ticket categorization tools assign appropriate labels and prioritization levels to customer inquiries, enabling your teams to prioritize urgent issues and meet your service level agreements (SLAs). Helpdesk ticketing platforms also route tickets to the appropriate tier levels, ensuring suitable agents with the right skills are handling them.
#6 Reduction in duplicate work and overlooked requests
The centralized system ensures visibility into the ticket statuses. Your teams can see who’s assigned to a task and if that person has started working on it. This effectively prevents any duplicate work.
#7 Easier identification of common issues and creation of knowledge bases
The tickets reveal common issues and frequently asked questions, providing information that can be used to populate the knowledge base.
You can then use the information bank for a FAQ section, enabling your customers to find answers on their own, and for an internal knowledge base your agents can use as an instructional guide for resolving issues.
#8 Improved team collaboration and knowledge sharing
Help desks come with internal collaboration tools that allow agents to work together seamlessly. Your teams can add internal notes to tickets, tag specialists who are equipped to address the comments, and communicate with other customer service reps without leaving the platform.
#9 Scalability to handle growing customer bases
With the help desk simplifying ticket organization and efficient resolution processes, your teams will have the bandwidth to handle large volumes of inquiries without sacrificing the quality of their service. And because the system automates your workflows, tickets get resolved much more quickly without drowning your agents in repetitive tasks.
#10 Enhanced customer satisfaction through faster response times
Help desks provide agents with insights that allow them to anticipate and meet customer expectations. They also enable faster resolution and enhanced service quality. Your customers are more likely to come out of the experience satisfied and with a positive impression of your brand.
You can only capture all these benefits if your ticketing system for customer service has the related features. In the next section, we’re going to help you learn what to look for.
Which ticketing system features should you focus on
When selecting a ticketing system, it's crucial to focus on features that will streamline your support process and enhance customer satisfaction. Here are some key features to consider:
1 Multi-channel support
The helpdesk ticketing solution should serve as a hub of all communication channels your customers prefer, such as email, chat, phone, and social media. This enables agents to view all customer interactions in one place and continue conversations without asking the same questions. This is basically what a ticketing software system is all about in customer service.
The ticketing system must also allow channel-specific routing and handling rules.
2 Ticketing automation
If you look at any top ticketing system example, you’ll see that all of them have automated ticket creation from all support requests and route them to the right agent or department based on the preset rules.
The automation in the help desk toolbox can assign incoming tickets with priority levels based on the customer status. It can also use certain keywords or trigger words to determine urgency.
Finally, your platform should be able to automatically send follow-ups to customers and reminders to agents.
3 Service level agreement (SLA) management
A good customer support ticketing system can track SLA metrics, such as first response time and resolution time, and send alerts that help ensure your teams are on track. It should also have pre-programmed escalation workflows, allowing your teams to take appropriate actions when SLAs are breached.
4 Ticket tagging and categorization
Ticket categories provide an overview of the nature of the ticket or issue. Some examples are technical issues, customer feedback, product inquiries, policy questions, and billing.
Your help desk should allow you to customize the classifications and automatically assign ticket tags. It should also enable nested categories (hierarchies and sublevels) for complex issues. Tag-based reporting will come in handy for analyzing trends.
5 Сanned responses
Canned responses (or macros) are predefined answers to frequently asked questions. Your help desk should come with a library of customizable pre-written messages and shortcut keys to enable quick replies. It should also include analytics for tracking the usage of macros and analyzing their effectiveness.
6 Customizable ticket status options
Ticket statuses (like open, pending, in-progress, overdue, closed, and canceled) allow your teams to track and account for the progress of the issue resolution. Your help desk should allow you to customize these labels to better match your teams’ workflows. You should also be able to automate status updates based on actions taken.
7 Customizable submission forms
Your help desk should come with drag-and-drop builders, which make it easy to create templates for different types of queries. It should integrate with your customer database to enable pre-filled information.
Your ticket forms should enable conditional fields (so they only reveal relevant fields to fill up), allowing your customers to populate them quickly. Multi-language functionalities are essential for catering to a global market.
8 Agent-facing knowledge base
Powerful ticketing platforms integrate knowledge base tools, enabling your teams to attach relevant articles to tickets. The platform can even automatically suggest solutions based on the content of the ticket.
Your teams can also use the information from tickets to build the knowledge base, using the system to identify common issues and queries. An analytics dashboard can help track the usage of the resources and measure their effectiveness.
9 Reporting and analytics
Your help desk should come with comprehensive analytics features that allow decision-makers to thoroughly analyze your support operations. It should include customizable dashboards for different roles and enable real-time tracking of performance metrics, trend analysis, and forecasting. You should be able to export the reports for further data analysis and easy file sharing.
10 Collaboration tools
Ticket platforms integrate collaboration tools designed to boost agent productivity and drive accountability. Your help desk should facilitate team communication with internal notes and @mentions. It should also link with team chat tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams.
Your teams should be able to do collaborative edits on the tickets, with everyone seeing the latest version. You should also be able to share the tickets and transfer their ownership when necessary.
11 Customer self-service portal
Take a load off your agents’ hands with a customized customer self-service portal that allows clients to access information and troubleshoot issues independently. Your customers should have easy access to your knowledge base, FAQs, and community forums.
12 Mobile accessibility
Provide your teams with the ability to manage tickets on the go. Choose a help desk that offers a dedicated mobile app. It should have a responsive interface, push notifications for urgent issues, and offline mode to enable working without an internet connection.
Next up, we’ll show you just how to choose a ticketing system with all the right features.
How to choose the right ticketing system for your business: 14 easy steps
It’s time to get down to the practical steps to help you land the ticketing service platform that matches your business needs.
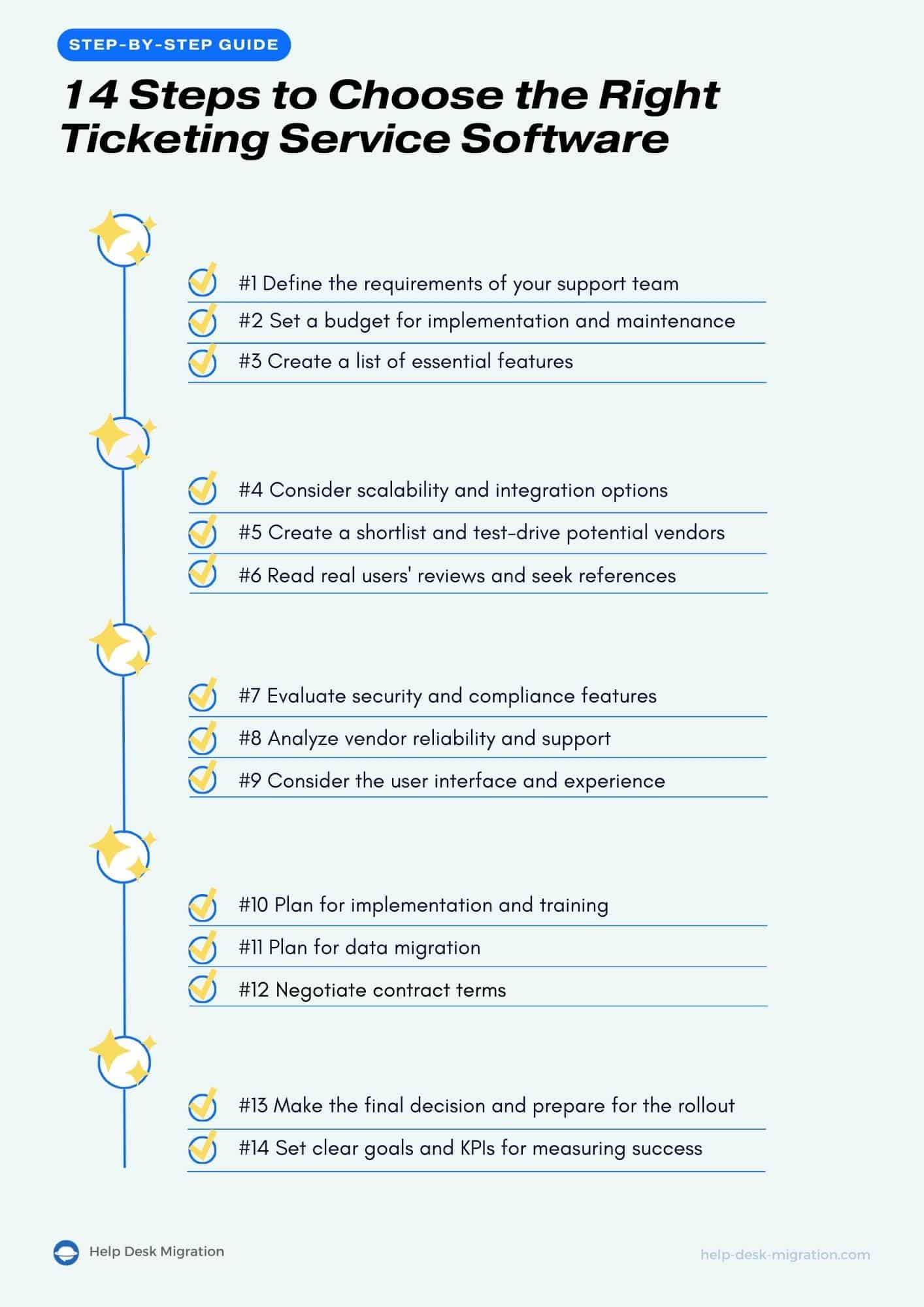
Step 1. Define the requirements of your support team
Start by assessing the needs of your support team. Conduct surveys and interview your agents to understand their pain points. Look closely at your existing workflows and identify ways to improve them.
Based on this information, list down the features that your help desk should have. You should also consider future scalability requirements and the technical capabilities of your team.
Step 2. Set a budget for implementation and maintenance
Before shopping around for the right customer ticketing software, calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) to avoid spending more than you can afford.
Consider the initial purchase or subscription costs, implementation and training expenses, ongoing maintenance and support fees, and potential upgrade costs. Make sure you’re leaving a budget buffer or cushion for unexpected costs or additional ticketing system features. Lastly, factor in the potential ROI in terms of improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Step 3. Create a list of essential features
Divide the ticketing system features you’ve identified into "must-haves" and "nice-to-haves". Your list of essentials must include automation capabilities to reduce manual work, reporting and analytics tools, customization options to fit your unique processes, and tools that meet industry-specific requirements.
Step 4. Consider scalability and integration options
Your customer ticketing software should match any expansion plans you might have for your business. Make sure it can handle additional ticket load. It helps to assess the vendor's roadmap for future developments. You should also check whether the help desk offers multi-language support if you plan to expand to foreign markets.
Check for API availability to ensure the support ticketing system is compatible with your existing tools and can easily integrate new solutions.
Step 5. Create a shortlist and test-drive potential vendors
Research vendors and shortlist those that match your criteria. Take a closer look at what they have to offer by trying out demos and free trials.
Make sure you rope in team members who will actually use the support ticketing system. Keep a scoring system handy, so you can weigh your options objectively.
Step 6. Read real users' reviews and seek references
Reading customer testimonials on the provider’s company website will not suffice to acquire a full understanding of all the nuances of your future help desk. Before you jump in, go to reputable software review sites like G2 and Capterra for reviews from real users who are already using the software.
Step 7. Evaluate security and compliance features
It’s your duty to protect the data of your customers. Assess the help desk software’s data encryption and protection measures, data backup and disaster recovery policies, and compliance with relevant industry standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Take control of your ownership of the data: choose a solution that will make it possible to transfer to other vendors without losing any data.
Step 8. Analyze vendor reliability and support
Look at your online ticketing platform provider’s market presence and financial stability to see whether they are going to stick around for the long haul.
You should review the availability of dedicated customer support to ensure you can count on their assistance if you encounter issues. Also, assess the quality and frequency of product updates, as these help ensure the software's security.
Step 9. Consider the user interface and experience
You need to choose software that both agents and customers will actually want to use. Check for the intuitiveness of the interface. The learning curve must not be too steep, allowing the end users to adopt the new support ticket system quickly.
Aside from the usability, you should also check for customization options to ensure the customer support ticketing tool maintains the identity of the brand.
Step 10. Plan for implementation and training
Take the time to discuss implementation timelines and processes with the vendor. Develop a change management strategy for your customer service team to ensure the deployment process goes smoothly. You may have to hire professional services or consultants.
Also, make sure your team knows how to use the new ticketing tool properly. So, take your time for training.
Step 11. Plan for data migration
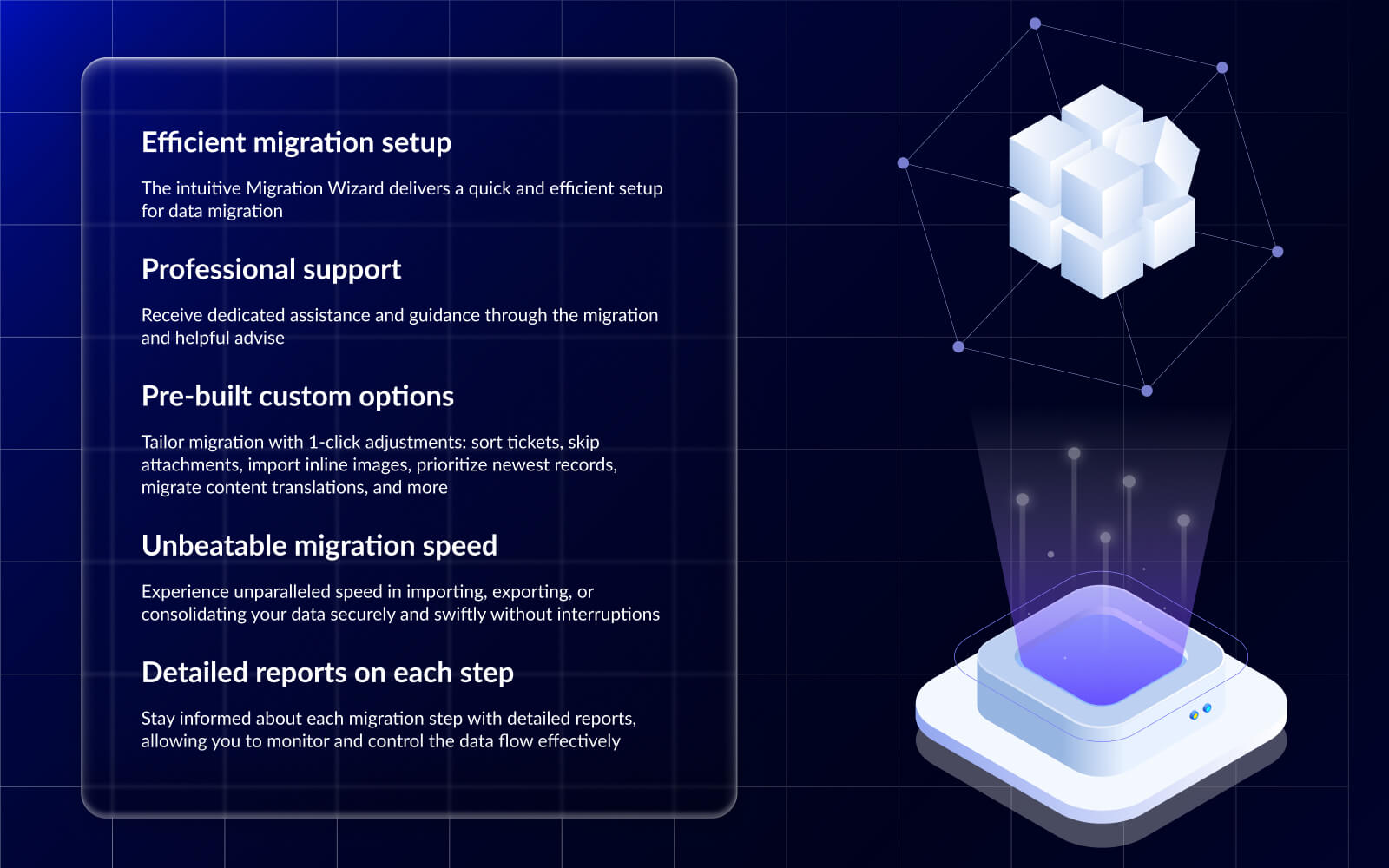
Adopting a new business ticketing system for customer service means moving to a new place with large amounts of data. That requires separate planning as you need to prepare data for the import, plan the timing, and run test migrations to tune the mapping between source and target systems. Besides, you might need to customize the standard workflow.
The Help Desk Migration service can handle all these aspects. Our team has thousands of successful migrations under its belt and can create the best-fitting plan for your case. With the Migration Wizard, you can set up the data transfer in just a few clicks and move your data automatically and securely.
Step 12. Negotiate contract terms
You need a foolproof contract to ensure all parties will meet their end of the bargain. It will also protect you from unexpected expenses.
Before signing on the dotted line, clarify all costs (including potential hidden fees), discuss SLAs for uptime and support, negotiate terms for scaling up or down, and discuss options for future customizations or integrations. It’s also important that you understand the contract renewal and cancelation process.
Step 13. Make the final decision and prepare for the rollout
Now that you have your ducks in a row, you can present your findings and recommendations to key stakeholders. Your goal is to make a collective decision based on all gathered information.
Once you’ve chosen a specific ticketing platform, you can start developing a more detailed implementation plan and data migration strategy.
If you enlist the services of Help Desk Migration, you can schedule a consultation to discuss your specific needs, perform a free trial Demo to ensure correct data transfer, schedule the Full Migration, and get your data to the desired ticketing system with zero downtime. These steps help ensure a quick, easy, and secure data import.
Step 14. Set clear goals and KPIs for measuring success
Early on, you should already plan for ongoing evaluation and optimization of the help desk system that you choose. That way, you can hit the ground running. It’s easier to find ways to improve when you track your performance metrics from the start.
Following these steps takes time and resources. But considering the costly mistakes this kind of planning helps you avoid, the benefits outweigh the costs.
Top 5 ticketing systems for exceptional support
After we review the benefits of ticketing systems, identify the core features to look for and discuss the steps to make the right choice, it's time for real-life examples. To help you with the decision-making process, we've listed the top five ticketing systems available that meet different preferences.
Zendesk
Zendesk is high-quality customer service software. It caters to companies of all sizes, particularly medium—to large enterprises in industries like e-commerce, technology, education, and healthcare. The help desk platform offers 5 pricing tiers, starting with the Suite Team plan at $55 per agent per month when billed annually.
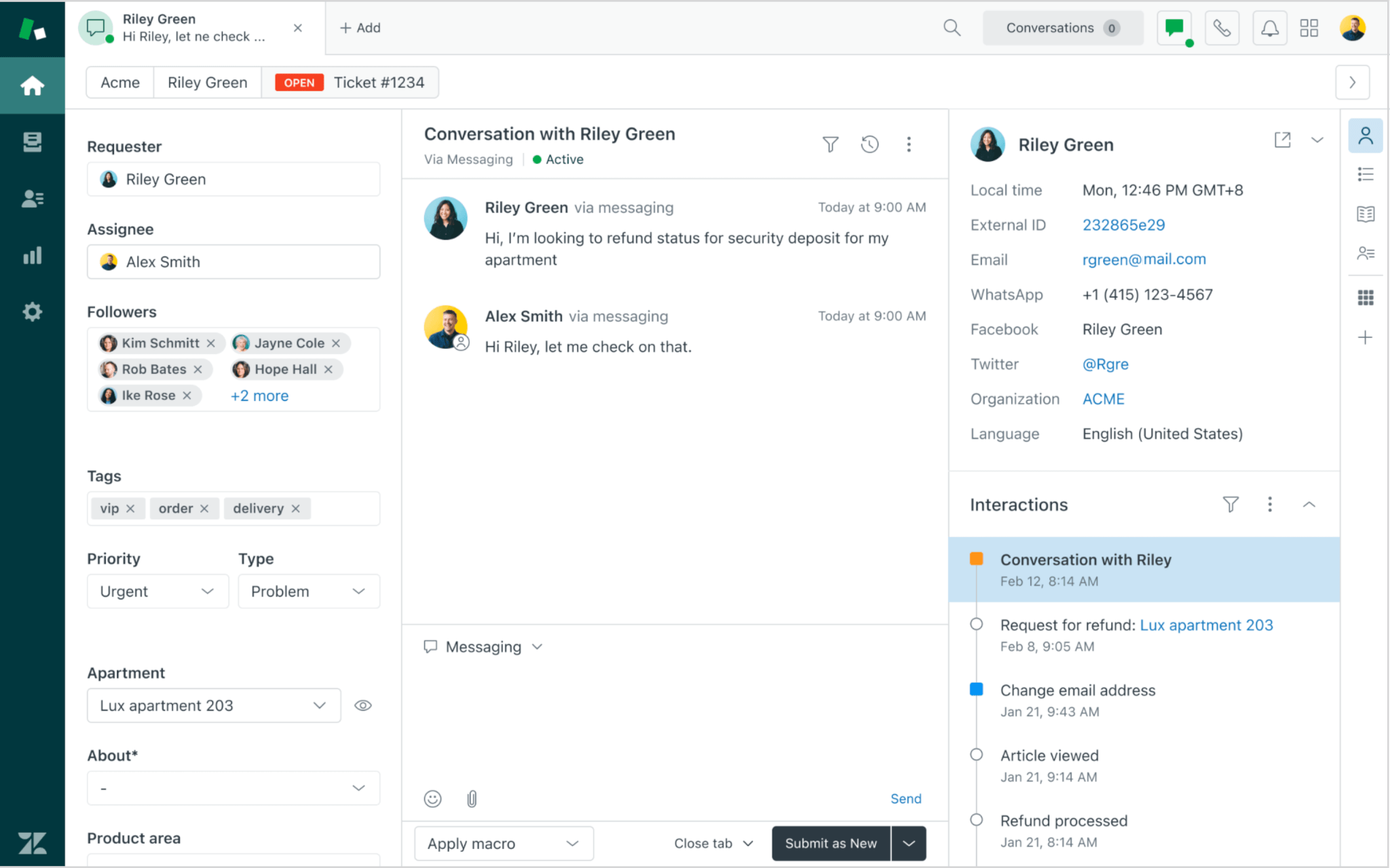
The ticket view in Zendesk. Source: Zendesk
The help desk platform delivers comprehensive features, including multi-channel support, Zendesk Answer Bot, AI-driven automation, and advanced reporting. Moreover, Zendesk Guide is a powerful asset for customers and support teams. It lets support teams create, organize, and manage a library of help articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides that are easily accessible with smart search capabilities. However, the costs can quickly add up with add-ons and higher-level plans, making it less suitable for small businesses or startups on a tight budget.
Freshdesk
Freshdesk is a robust ticketing system suitable for small to medium businesses in the retail, technology, and education industries. Its pricing plans start with the Free plan for basic features, which is ideal for startups or small teams. The Growth plan, which includes more advanced features, starts at $15 per agent per month when billed annually.
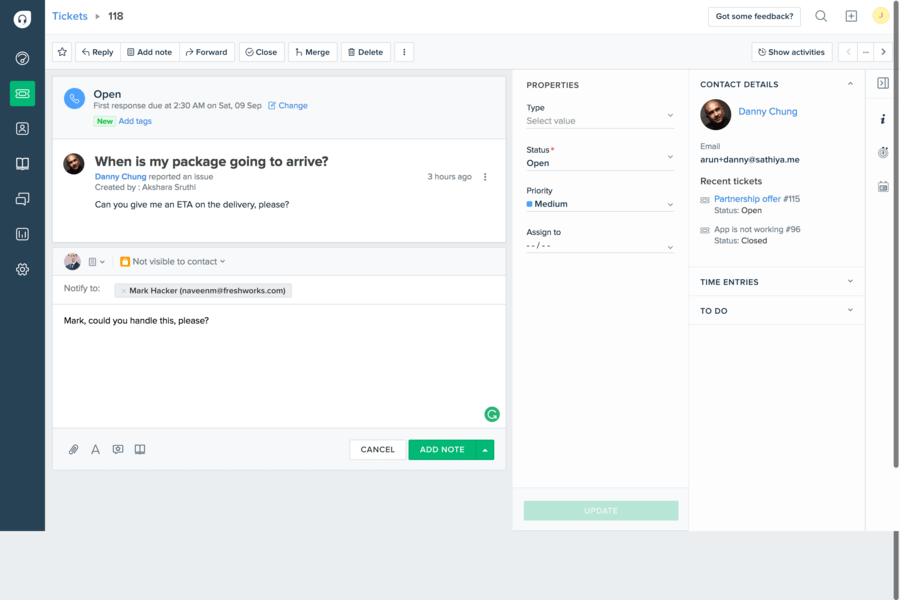
The ticket view in Freshdesk. Source: Freshworks
Freshdesk brings all conversations together in one place so that customer service agents can easily see previous interactions and provide better assistance. With tools for collecting customer feedback and personalizing support, it helps improve the overall service experience. Additionally, Freddy Insights, powered by artificial intelligence, provides support managers with intelligent insights into team performance. However, the platform's extensive customization options can be overwhelming, and many advanced features are often locked behind higher-tier pricing plans. Besides, the lack of some essential third-party integrations may limit workflow efficiency.
HubSpot Service Hub
With HubSpot Service Hub, you can create and manage tickets from multiple channels, all organized and tracked within customizable ticket pipelines or workspaces. HubSpot Service Hub is popular among small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs), startups, and growing enterprises in SaaS, e-commerce, and B2B services. It offers 6 pricing options starting at $0 for the Free Tools, which include basic ticketing and customer service features. The Starter plan, $15 per month per seat, features more advanced features like live chat, ticket automation, and conversation routing.
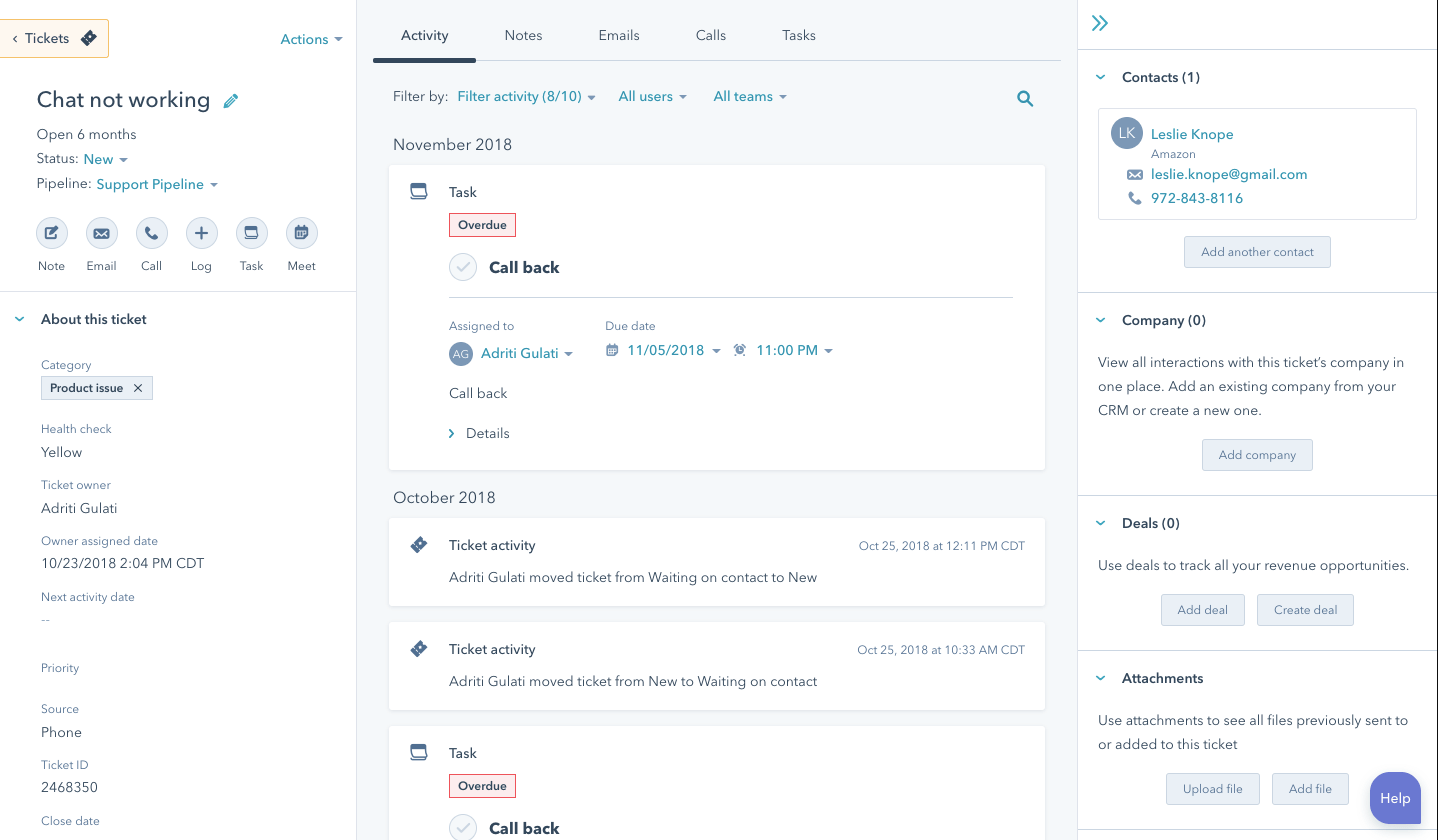
The ticket view in HubSpot Service Hub. Source: HubSpot
This customer support platform is perfect for sales teams. It integrates with HubSpot's CRM, marketing, and sales tools to deliver a unified customer experience. HubSpot Service Hub features include advanced reporting, knowledge base creation, Conversation Intelligence, customer feedback surveys, and personalized ticket views. However, HubSpot Service Hub does have some limitations. Lower-tier packages lack customization and advanced automation capabilities. Additionally, teams unfamiliar with the HubSpot ecosystem might face a steeper learning curve.
Front
Front is an AI-powered customer service platform that excels in collaboration and communication management. It is well-suited for e-commerce, SaaS companies, marketing agencies, and consulting businesses. Front's pricing starts at $19 per user per month for the Starter Plan (up to 10 seats), with more advanced plans available, depending on the features included.
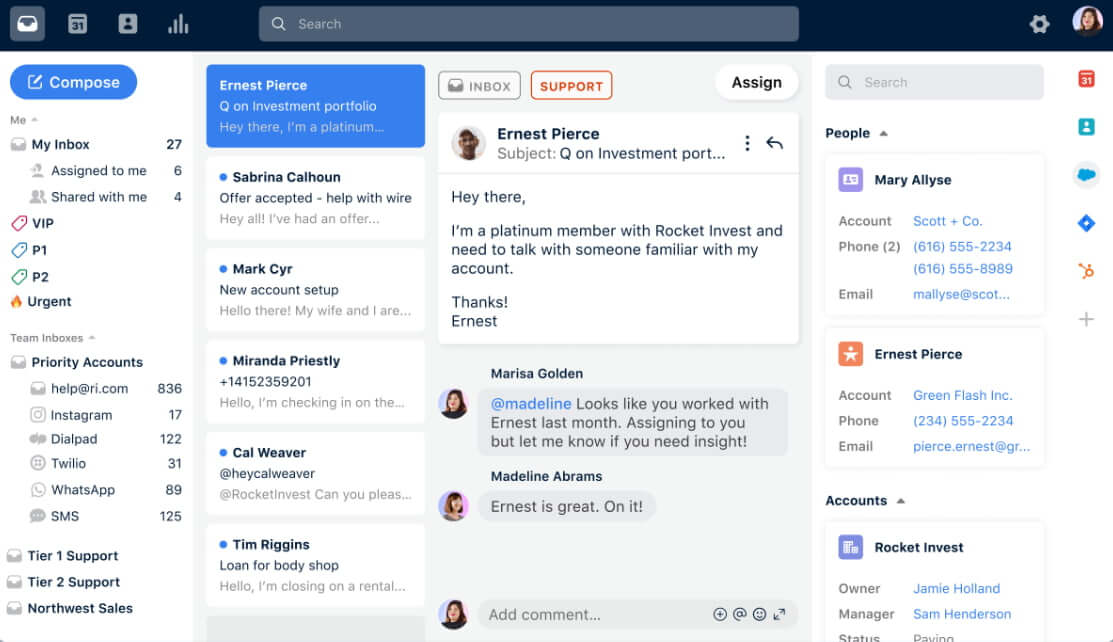
The ticket view in Front. Source: Front
Front's unified inbox consolidates emails, chats, and social messages and provides options to tag conversations, filter by priority, and create custom views. Its real-time collaboration tools include features like internal comments on messages, the ability to assign conversations to specific team members, and automated workflows that trigger responses based on customer interactions—all aimed at ensuring inquiries are handled efficiently and promptly. On the other hand, Front lacks integrations, which can hinder the user experience. It also requires a paid subscription, and the setup process can take a while.
Intercom
Intercom is a help desk platform tailored to businesses that prioritize real-time, personalized interactions. It caters to industries such as tech, SaaS, and e-commerce. Intercom's pricing starts at $29 per month per seat for the Essential Plan, which is ideal for individuals, startups, and small businesses.
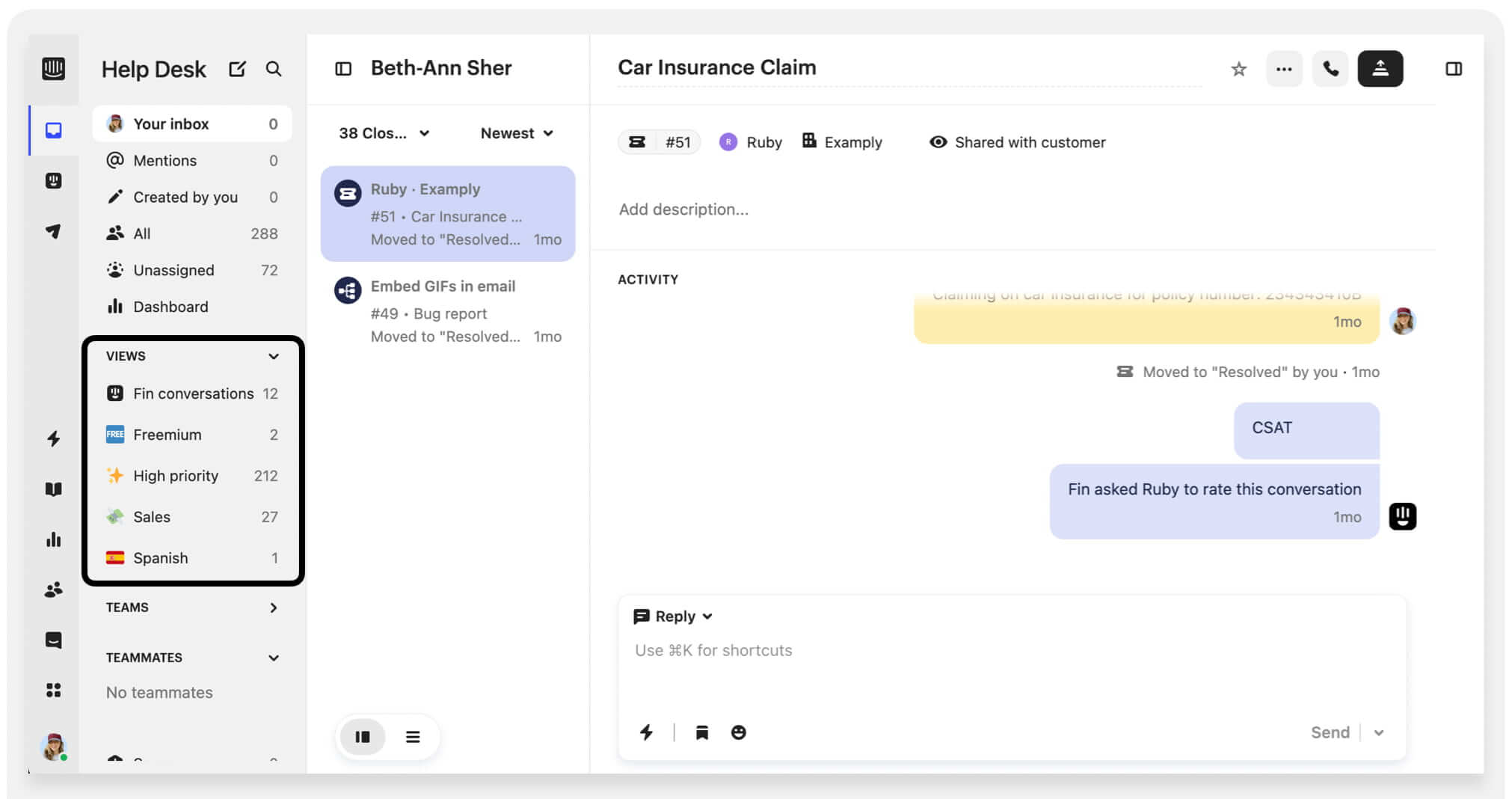
The ticket view in Intercom. Source: Intercom
This ticketing system offers a shared inbox, AI-enhanced workspace, live chat, automated messaging, and targeted campaigns. Its Fin AI Agent delivers comprehensive customer support through multiple knowledge sources and a centralized knowledge hub. It personalizes interactions with the desired tone of voice and offers real-time assistance. However, this help desk software has some drawbacks, including its high pricing and a lack of specific customer service features.
Recap
A good help desk system can up your customer service experience. It helps ensure you’re prioritizing urgent tickets, and that no customer issue falls through the cracks. It also equips your support teams with the tools they need to provide quick answers to queries and fix problems promptly.
But not all ticketing platforms are created equal, and not all businesses have the same requirements. You need to know which features to look for, which you need, and what steps to take to establish the best match for your business and get set up.
An important step in preparing for your new help desk is planning for the secure transfer of your data. Help Desk Migration can help you get sorted, whether you want to check out our services, book a call to discuss your needs, or test the data migration tool in a free trial.
FAQs
A ticketing system manages customer support requests (tickets). Here's how it works:
- Multichannel Support: The ticketing system consolidates requests from various channels into a single interface.
- Ticket Routing: Tickets are automatically assigned to the appropriate support agents based on predefined rules.
- Automation: Set up automated responses for common inquiries and workflows can streamline ticket handling, reducing manual effort.
- AI Integration: Use AI to analyze ticket data, predict issues, and enhance customer interactions through smart suggestions and automated ticket classification.
- Reporting and Analytics: The ticketing system tracks ticket trends and performance metrics, helping improve support processes.
- Integrations: Many ticketing systems integrate with other solutions (e.g., CRM, knowledge base, project management tools) to provide a more comprehensive customer support experience.
It streamlines support processes, enhances response times, and increases customer satisfaction.
A ticketing system improves support efficiency by:
- Centralized Communication: All inquiries are tracked in one place, making it easier for agents to manage requests.
- Prioritization: Tickets can be prioritized by urgency, ensuring critical issues are addressed first.
- Automated Responses: Automatic acknowledgments keep customers informed and engaged.
- Knowledge Base Access: Integration with knowledge bases helps agents quickly find solutions, speeding up resolution times.
- Performance Analytics: Provides insights into metrics, helping identify areas for improvement.
- Collaboration: Agents can assign tickets and share notes, fostering teamwork for complex issues.
- Self-Service Options: Customers can access FAQs and forums, reducing incoming ticket volume.
A ticketing system benefits various businesses, including customer support teams, IT and tech companies, SaaS providers, healthcare organizations, educational institutions, and more. Any business that handles customer inquiries or service requests can streamline communication and issue tracking with a ticketing system, improving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
A help desk is a comprehensive solution with various tools and features for managing customer requests and internal support. It usually offers ticket management, knowledge bases, live chat, and reporting. The help desk solution focuses on improving the overall customer experience and service delivery.
On the other hand, what is a ticketing system? A ticketing system manages and tracks customer requests (or tickets), focusing on organizing and streamlining the customer support process. Standard features include ticket categorization, status updates, automated workflows, reporting and analytics, and integration with other tools.
Yes, ticketing systems can effectively be used for internal IT support. They centralize communication, track issues, and improve accountability. Ticketing systems also simplify the process of reporting and resolving IT issues, improving overall service delivery.
You can customize a ticketing system to fit specific requirements by doing the following:
- Create custom fields based on your business needs (drop-down menus, multi-select options, date fields).
- Automate ticket assignments based on categories or agent availability.
- Set up SLA (Service Level Agreement) rules to prioritize urgent tickets.
- Define user roles (e.g., agents, managers, admins) and set permissions to control certain features and data access.
- Connect your ticketing system with email, chat, or social media platforms to centralize customer interactions.
- Develop custom reports to analyze ticket volume, response times, and agent performance. Use dashboards to visualize key metrics.
- Add post-ticket surveys to gather customer feedback and adjust processes accordingly.
- Conduct training sessions for your team to familiarize them with the ticketing system.
- Connect the ticketing system with preferred tools and add-ons for better efficiency.
To ensure a seamless transition to a new ticketing system, follow these steps:
- Select a Migration Date: Choose a time that minimizes disruption for your team.
- Keep Your Team Informed: Regularly communicate updates about the migration process.
- Organize Records: Review and clean up your current data in the Source ticketing system.
- Configure Target Platform: Set up the new ticketing system according to your requirements.
- Run a free Demo Migration: Test the migration process with our Migration Wizard.
Help Desk Migration simplifies the switch by importing customer service data with just a few clicks. Sign up for a free trial and see for yourself.


