Help desks can take many different forms, depending on your company’s specific needs. They may be designed to cater to external customers, or they may be configured to provide seamless tech support to your employees. A help desk manual clearly defines how to properly set up and operate the system so it fully meets the unique requirements of your organization.
In this article, we’ll talk about why your company needs a help desk manual and how you can go about creating and using one. First, we’ll give you a help desk manual definition so we are all on the same page.
What’s a Help Desk Manual, and Why Do You Need It?
Because help desks are designed to meet the unique needs of businesses, there’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to their workflows and structures. Hence, your teams need a help desk manual to learn their way around a specific system.
A help desk manual provides detailed guidelines to help users navigate the platform. It outlines the ins and outs of the help desk system, showing you how to set up the platform and operate it so your team can provide high-quality support without fail.
The manual will show how to connect your communication channels, create routing options for your team’s specific workflow, assign tags, set automation rules, and whip up knowledge bases, among others. As a result, support desk employees of all ranks and roles won’t require any handholding. Plus, the onboarding process for new hires will be straightforward.
Who Uses a Help Desk Manual?
While everyone in your company could benefit from a help desk manual, employees with the following job roles need them the most or use them more often.
- Help desk administrators. They are responsible for the configuration of your help desk system and troubleshooting issues. They set up advanced settings, add new users, and integrate third-party apps. A comprehensive manual enables them to do it the way it works for your needs.
- Heads of the support department. These experts are accountable for the overall performance of the department. A manual helps department heads keep the help desk operations of all teams aligned, as it describes all the workflows, procedures, and processes in detail.
- Support representatives. They are the ones who interact directly with the customers. And because customer experience can make or break a business, it’s vital that your support representatives are adept at providing stellar services. A help desk manual will provide your agents with the in-depth guidelines they need to do their job effectively and consistently.

What Does a Help Desk Manual Include?
Since manuals come in different forms, tailored to different needs, there’s no one-size-fits-all standard.
For example, a technical help desk manual for administrators has detailed instructions on how to configure and operate your system. Meanwhile, a customer services one for support reps details how your agents should respond to tickets by providing canned responses, detailing proper phrasing, and setting standards for communicating in various scenarios. Finally, an IT help desk manual gives your ITSM department detailed instructions for troubleshooting incidents. There are also universal manuals that address different needs.

Here are some suggestions on what you can include in your manual.
Ticket Statuses
Get your tickets moving quickly through all phases of the lifecycle with statuses clearly defined in your manual. Here are the most common ticket statuses:
- New: Every ticket created through your system will be marked new.
- Open: An open status indicates that an agent or specialist is working on the ticket.
- Pending: A ticket is marked pending if the agent is waiting for the customer to provide more information.
- Escalated: This is to specify that the ticket has been escalated to a supervisor or another department.
- Resolved: This means the ticket has reached the final stage of the lifecycle and requires no further action.
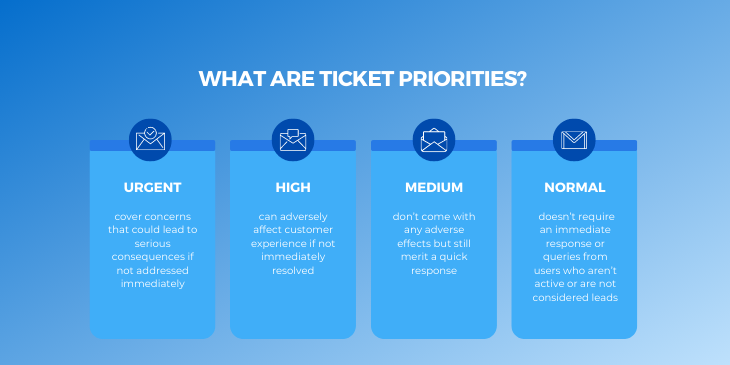
Ticket Priorities
To stay on top of their responsibilities, your agents need clear guidelines on which tickets to prioritize. Here are the standard prioritization levels.
- Urgent. Urgent tickets cover concerns that could lead to serious consequences if not addressed immediately. They must be on top of the agents’ queue or escalated to a supervisor.
- High. High-priority tickets can adversely affect customer experience if not immediately resolved.
- Medium. Those with medium priority don’t come with any adverse effects but still merit a quick response, mostly because they’ve already spent a certain amount of time in the queue.
- Normal. Tickets with a normal priority level include customer feedback that doesn’t require an immediate response or queries from users who aren’t active or are not considered leads.
Processes
Your agents should have a clear picture of what the entire workflow looks like, from the moment a customer submits a ticket to the time it’s resolved. That way, they know exactly what actions they’ll have to take.
- Response to tickets. Have clear guidelines on how your agents should respond to a customer’s first message. Should they send an acknowledgment email? What details will it include?
- User follow-up. Specify what the agents should do next and format a follow-up email that they can send in case there’s no response from the customer after a specific period of time.
- Closing tickets. Be clear about when the tickets can be considered closed. You should also add guidelines for sending CSAT surveys.
- User feedback. Be ready with actions that the agents can take in case customers are not happy with the service they received.
Ticket Escalation
Not all tickets make a smooth journey from initiation to resolution. You need to have a plan for those that require the help of a supervisor or a specialist. The escalation process often involves the following.
- Clearly define issues that require escalation.
- Identify the supervisors or specialists who will receive or handle the escalations.
- Set a timeframe for resolving the tickets. Check with your company’s service-level agreements (SLAs).
- Set a schedule for sending updates to customers.
- Name the persons to contact if the issue remains unresolved.
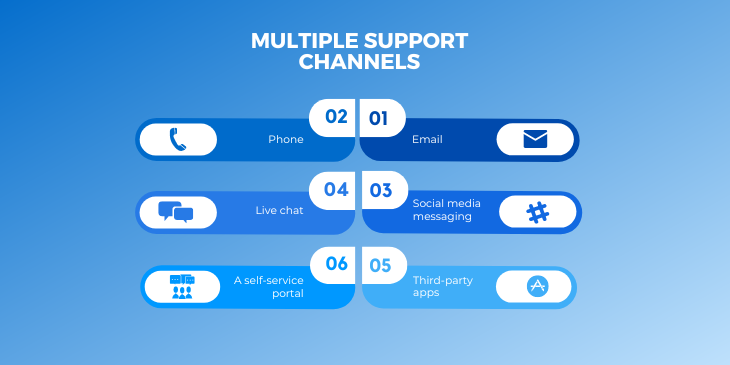
Support Channels
Most help desks integrate multiple support channels, including email, phone, live chat, social media messaging, a self-service portal, and third-party apps. Your manual should explain how each channel will be configured and connected to the help desk platform.
Automation Rules
To maximize workflow efficiency and agent productivity, your help desk software must automate processes wherever possible or advisable. At the very least, the system should include action- and time-triggered automation rules. Your help desk manual is there to itemize all the automation options and explain how to configure them.
Service-level Agreements (SLAs)
The performance standards you set for your support team must be in keeping with your company’s SLAs. To ensure your agents are always steered in the right direction, your help desk manual must clearly lay out your SLA policy.
Macros or Canned Responses
To streamline workflows, be ready with macros or message templates that will enable agents to quickly respond to common queries. This will speed up ticket resolution and save a lot of time for your support team.
Analytics and Reporting
Help desk systems have analytics and reporting features that let you track certain metrics and KPIs. Use them to reach goals and improve the performance of your agents. Your manual should specify the reporting options available at your help desk and the ways to configure them. It should also name the employees responsible for managing your help desk statistics.
Team Management
You can organize your support team into departments that will handle specific types of customers. For example, you may have a specific department for VIP customers or for those coming from a specific country. You can then assign agents who will specialize in handling those specific customer types. Your help desk manual should show you how to create and edit departments, add and remove relevant agents, automate the routing of tickets, and monitor how each department is performing.
Conclusion
Without detailed help desk procedures, your platform may not be the efficient tool it’s supposed to be. So, make sure your teams are equipped with help desk manuals that ensure they’re doing their job properly. The usefulness of your system boils down to proper execution. And manuals provide clear guidelines that can help ensure that.


