Whether you like it or not, your business is going to encounter problems that disrupt your normal service operations. While you can’t stop them from happening entirely, you can control how you respond.
Effective incident management is what makes the difference between a problem that goes away quickly and a catastrophe that leaves an enduring impact on your business.
What is incident management? In this article, we’ll define what incident management means in the technological realm. We’ll also recount the benefits of giving it ample attention and the challenges you may encounter along the way.
Of course, we’ll show you how to improve your incident management procedures and give you a list of the best tech tools to help your teams develop an effective plan.
What is an incident? What is incident management?
Before we answer the question, “What is incident management?” let’s first define an incident.
In the world of IT support, an incident refers to unexpected disruptions to normal business operations or service delivery. The problem can be as minor as a temporary system downtime or as severe as a data breach that exposes sensitive information.
Incident management aims to fix issues and return operations back to normal as quickly as possible, with minimal impact on the business.
Benefits of implementing incident management
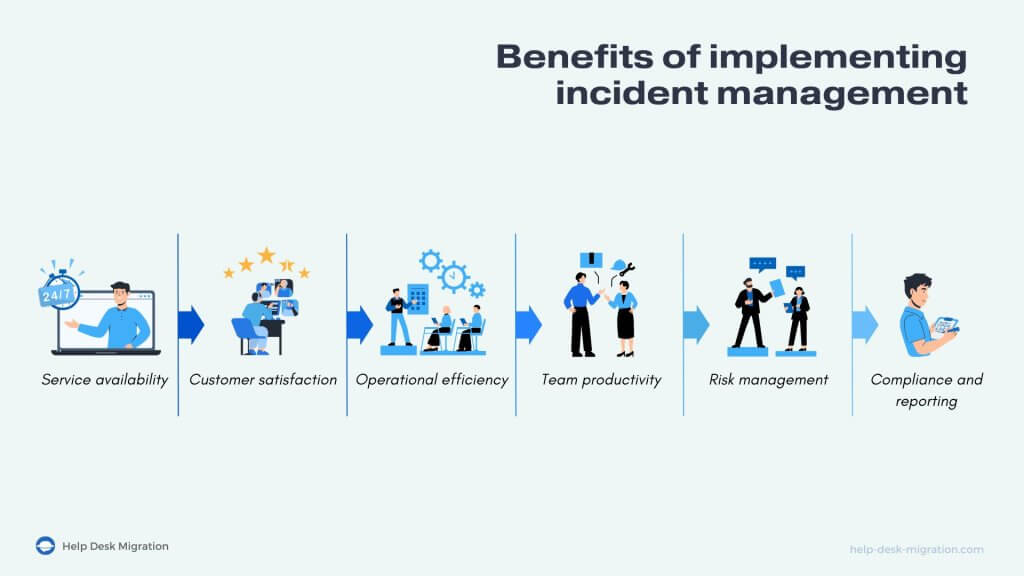
Implementing the best practices for incident management offers numerous benefits:
- Service availability. Effective incident resolution minimizes downtime.
- Customer satisfaction. Prompt resolution of issues brings greater satisfaction to your end users.
- Operational efficiency. Clear incident response plans allow your business to quickly go back to normal operations and minimize wasted resources.
- Team productivity. Quick incident resolution allows staff and stakeholders to go back to focusing on their core tasks.
- Risk management. Your organization will get better at identifying vulnerabilities and deterring potential risks.
- Compliance and reporting. Efforts to maintain detailed records and incident reviews will help you stay compliant with industry standards.
The process of incident management isn’t without its challenges.
5 Common challenges of incident management
Central incident management best practices involve anticipating challenges and confronting them head on. Here are the key ones to look out for:
1 Escalation plan for preventing potential incidents
Without an escalation plan in place, your teams could be scrambling for solutions when critical incidents occur. You need an established framework that they can follow to quickly resolve potential issues.
The strategy must also pre-empt problems so your teams can confront and resolve them before they even happen. It helps to have monitoring systems that alert you to a minor service interruption, allowing you to bring in specialists who can nip it in the bud before it becomes a major incident.
2 Staff utilization
Your staff must know their specific responsibilities and have clear protocols to follow. Otherwise, they could end up duplicating each other’s efforts or causing delays as they wade through the confusion. You also won’t know who to hold accountable if you don’t properly assign key roles and responsibilities.
3 Cost
Organizations may hesitate to pour resources into incident management because of budget constraints. But failing to invest in it could even be more costly. After all, service downtime, compliance fines, and SLA breaches come at a hefty price.
4 Clear channels of communication
Without clear communication lines, your staff could lack visibility into what’s happening. Critical incidents could fall through the cracks. And your teams could easily revert to damaging blame games, wasting valuable time when the actual problem is in full scale. Additionally, a lack of updates can lead your clients and stakeholders into a state of panic.
5 Testing workflows with simulated incident scenarios
You could spend a lot of time and resources on an incident response plan only to later realize it doesn’t work. Simulating potential incidents can help you test your plan. You’ll be able to spot flaws and make improvements. Failure to do this could have you learning expensive lessons during an actual, full-blown incident.

Knowing just what to expect helps you stay prepared.
What is a typical incident management workflow?
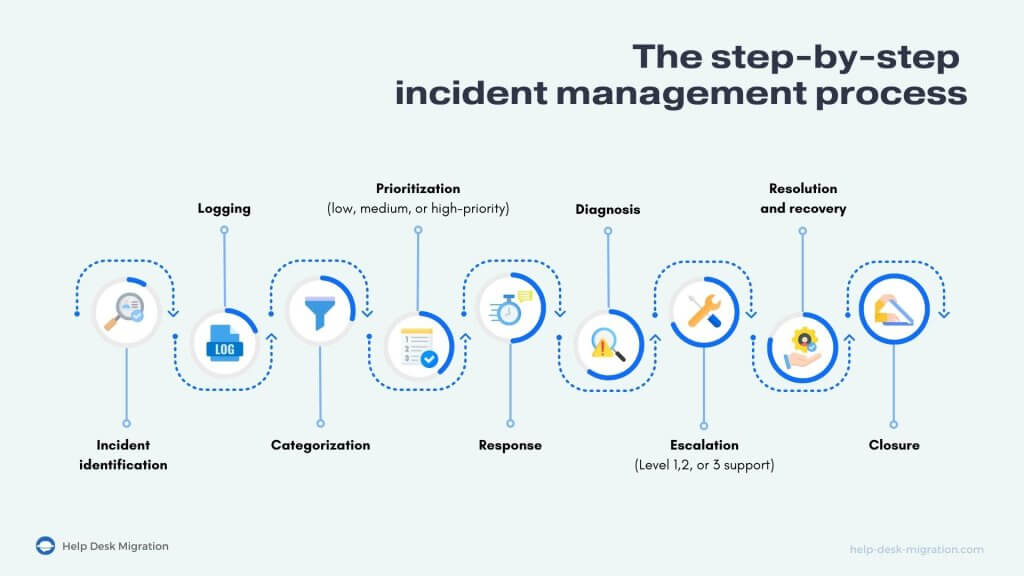
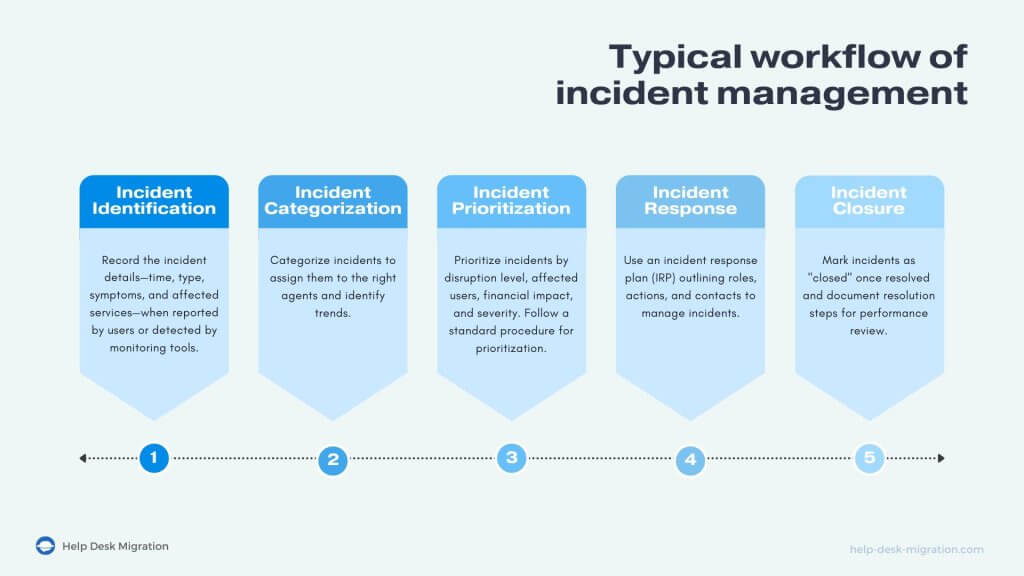
Incident management follows a protocol that starts with the identification of an incident and ends with your team closing the case. Let’s take a closer look at all the stages of a typical workflow.
Incident identification
The incident management procedure starts with an issue being reported by an end user. The incident may also come to your attention via tools that monitor and sound alerts.
It’s important that your teams properly identify and record the disruptive incident. Take note of the time of occurrence, type of incident, symptoms of the problem, and affected services. Proper recording in the initial stages can help make later steps and eventual resolution much easier.
Incident categorization
Categorizing incidents helps ensure tickets are assigned to the right agents. It also allows your teams to identify trends and patterns that you can later use to improve your processes.
Incident prioritization
Some incidents are more disruptive than others and should be treated with a corresponding level of urgency. Incident prioritization helps ensure your teams are paying greater attention to the more impactful incidents.
Set a standard operating procedure for assigning prioritization levels to incidents. It should check the number of affected users, the potential financial impact of the incident on the company, and the severity of the security and compliance breaches.
Incident response
Now that the incident has been properly classified and assigned, it’s time to get down to actually resolving it. You should have an incident response plan (IRP) in place. An IRP is a written document that directs how your teams should act before, during, and after an incident. It must clarify roles and responsibilities, provide clear guidelines on actions to take, and list the key people or stakeholders to contact for specific crises.
Incident closure
Agents need to mark incidents “closed” once they’re resolved. This ensures they’re officially removed from the queue (and not creating clutter!). The assigned agents must also document the steps they took to fix the problem. These records will allow you to review and assess the performance of your teams and make improvements where necessary.
Each of these stages of the workflow entails a number of substeps. We’ll consider these in the next section.
Incident management checklist
Allow this checklist to guide your teams along the way. It will help ensure you’ve got all the incident management process steps covered.
Preparation
- Define incident criteria (come up with ticket classifications).
- Develop an Incident Response Plan (prepare detailed instructions and guidelines that your teams can easily follow).
- Implement incident management tools (equip your teams with help desks complete with automation and collaboration tools).
- Train the incident management team (make sure your teams have the right skillsets).
- Establish communication channels (set up a command center for communicating your plans, escalating issues, and sending progress notifications).
Incident detection and reporting
- Monitor systems for potential issues (proactively detect system disruptions).
- Incident identification (confirm the occurrence of an incident).
- Incident logging (keep a detailed record of the incident, complete with the time of occurrence and its symptoms).
Incident classification and prioritization
- Classify incidents (assign tickets to the proper categories).
- Prioritize incidents (assign an appropriate priority level to every ticket).
Incident assignment and escalation
- Assign the incident to the appropriate team/agent (make sure tickets are being routed to the right tier).
- Monitor the incident status and escalate if necessary (escalate complex problems to appropriate IT specialists).
Investigation and diagnosis
- Investigate the incident (confirm the initial diagnosis and look into the root cause of the incident).
- Document the findings (prepare detailed documentation of the official diagnosis).
Resolution and recovery
- Develop a resolution plan (create a resolution plan that’s specific to the diagnosed problem).
- Implement the resolution (follow the resolution plan to fix the problem).
- Verify the resolution (check and confirm that the issue has been resolved).
Closure and review
- Close the incident (file the ticket as resolved).
- Conduct a post-incident review (perform a postmortem analysis to assess the performance of your teams and figure out ways to prevent the incident from happening again).
- Update the documentation and the incident management process (figure out if there’s room for improvement and make changes where necessary).
Keep this checklist handy as you work on improving your incident management process.
Incident management best practices: 9 tips to check
You can have an ideal incident response plan in place but still fall short if you fail to implement it properly. Apply the following incident management best practices to get the best results.
1 Create teams with the right skills and train them
You need to bring together people who have the necessary skillsets. What this looks like will depend on your product offerings. Your team may include internal IT employees, cross-functional stakeholders, and third-party service providers.
Make sure you clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each member. You should also provide guidelines on how they must act before, during, and after an incident is identified.
Don’t just leave your teams to learn the ropes. Train them to resolve incidents effectively and quickly and empower them with the right tools. Maintain regular sessions to ensure they’re always updated with the latest technology. You can also sponsor enrollments in certification courses, such as Google IT Support Professional Certificate, ITIL® 4 Foundation, and CompTIA A+.
2 Define your incident management vocabulary
Jargon in the tech world is so dynamic that it can easily create confusion. Adding in people from various departments can create even more mayhem.
This is why your incident management strategy and response plan must include predefined terminology that’s precise and actionable. This helps ensure there’s no room for misinterpretation, allowing team members to quickly and accurately respond to incident management alerts and guidelines.
3 Establish a communication channel
You need a command center for communicating your incident plan, escalation strategy, and progress. Service desks or ITSM (IT service management) systems work well for this purpose. You can use them to send out alerts to the right team members, communicate escalation statuses, and assign tasks.
The system must have all the necessary contacts and schedules of resolvers and stakeholders. It must have clear guidelines on who to contact when an incident arises. For instance, your teams must only alert stakeholders for high-level issues, while the resolvers must have visibility on the whole incident management process.
4 Cultivate the right support culture
For incident management to be effective, you can’t just focus on processes and tools. You also need to pay ample attention to the human side of things. Create a culture that encourages people to focus on solving problems instead of assigning blame. Instead of determining who caused the problem, the initial response should be to look for what’s causing the disruption and to determine how to fix it.
Your teams must also get into the habit of learning from every incident and taking ownership of their role in it.
5 Adopt automation in your incident management
You can rely on your ITSM system to automate some of your incident management processes. It can assign tasks to the right specialists, facilitate communication between team members, and streamline workflows. It can even provide end users with canned responses to help them solve minor issues.
Service desks also provide reports that enable you to perform postmortem analytics. Reviewing the incident and understanding its root cause will help you take the necessary precautions to avoid a recurrence.
6 Prioritize incidents based on their impact
Specialists confronted with too many incidents may end up working on those they can finish easily, failing to pay ample attention to the more urgent ones. This is why it’s crucial to assign priority levels. You need to take into account the impact (severity of its consequences) and urgency (time sensitivity) of every incident.
7 Revamp your internal knowledge base and keep all documentation updated
Your internal knowledge base should be so effective that tickets are resolved quickly. If you are seeing a surge of incidents that are staying in queues a little too long, it may be time to revamp your self-service content. Here are some steps to take:
- Make sure the most searched and viewed articles are at the top.
- Keep your FAQ pages easy to read and scan.
- Collect feedback from the IT end users and make improvements where necessary.
Regularly update your documents to ensure they’re keeping up with the needs of your teams.
8 Test and review your incident response, and don’t skip root-cause analysis
Testing your incident plan can help you improve it. Simulate various incident scenarios, assess the effectiveness of your responses, and make changes where necessary.
You should also review actual incidents as they happen. This is vital to understand their root causes and figure out ways to keep them from happening again.
The key here is to be intentional and strategic with your incident management approach, so you don’t only react to issues as they happen but actually take proactive measures to minimize their impact and prevent recurrences.
9 Have an internal system for regular updates and logs
Sending out regular updates is an integral part of an efficient incident management system. Keeping IT clients and end users informed of how your incident response is progressing will prevent them from stressing out and bombarding your teams with queries. Your service desk should come with alert systems that automate these notifications.
But beyond applying these incident management best practices, you must equip your teams with the best tech tools.
10 ITSM and service desk platforms to build a successful incident management process
There is no shortage of ITSM tools to help your teams. Your problem will actually lie in choosing the most suitable ones. To help you out, we’ve rounded up the tools that should be at the top of any list.
Jira Service Management
Jira Service Management, part of the Atlassian suite, is a powerful IT service management solution designed to enhance collaboration between IT, development, and business teams. It combines robust incident, problem, change, and service request management capabilities with agile project management features from Jira Software. This integration allows teams to streamline IT operations, improve service delivery, and align IT with business goals effectively.
Source: Atlassian
Features that attract attention:
- Customizable workflows for incident, problem, and change management
- Integration with Jira Software for development teams
- Real-time collaboration and communication tools
- Automation rules to streamline processes
- ITIL-certified practices
Zendesk for Service
Zendesk for Service is more than just a customer service platform—it's a robust IT service management solution designed to streamline your IT operations. Whether you're tackling incidents, resolving problems, or managing changes, Zendesk offers intuitive tools that empower your IT teams to deliver exceptional service efficiently. Its seamless integration with other Zendesk products and third-party applications ensures flexibility and scalability, making it an ideal choice for organizations aiming to elevate their IT service delivery.
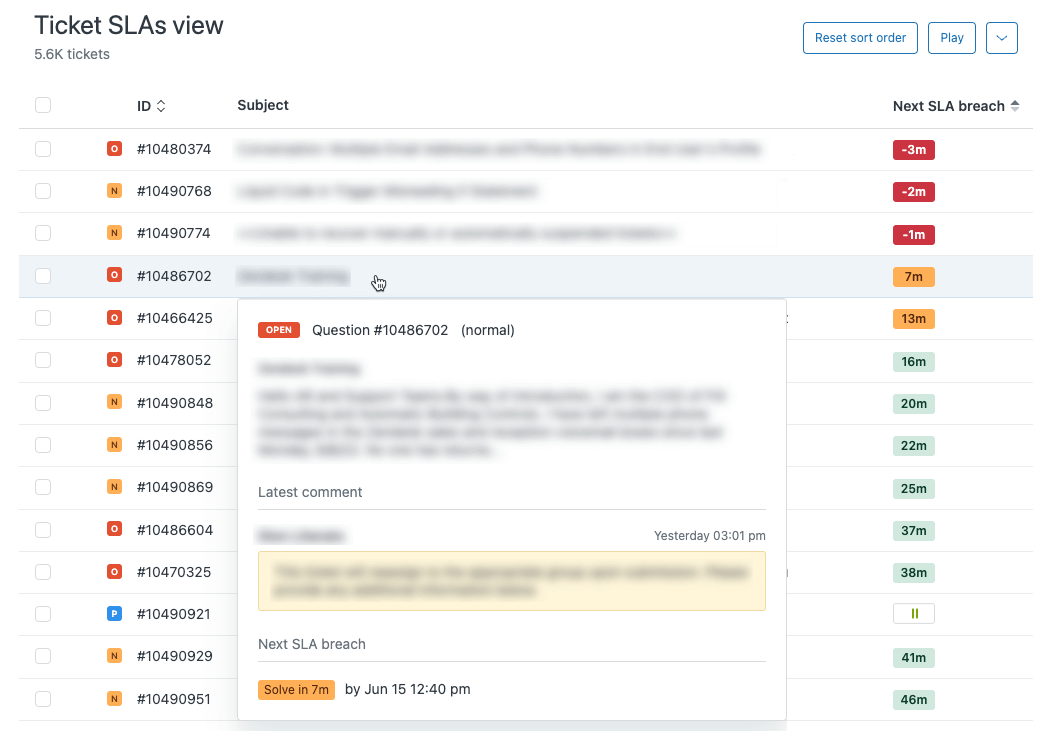
Source: Zendesk
Features that attract attention:
- Incident management and ticketing
- Automated workflows and triggers
- Self-service portal and knowledge base
- Integration with various third-party apps
- Analytics and reporting
Freshservice
Freshservice uses AI-driven tools to simplify enterprise-level service operations. Its cloud-based ITSM platform is easy to set up and use. It has powerful incident management capabilities and boosts your teams’ efficiency with integrated asset management. It also enables access to various tools from a single command center. An intuitive portal automates repetitive queries and enables self-service.
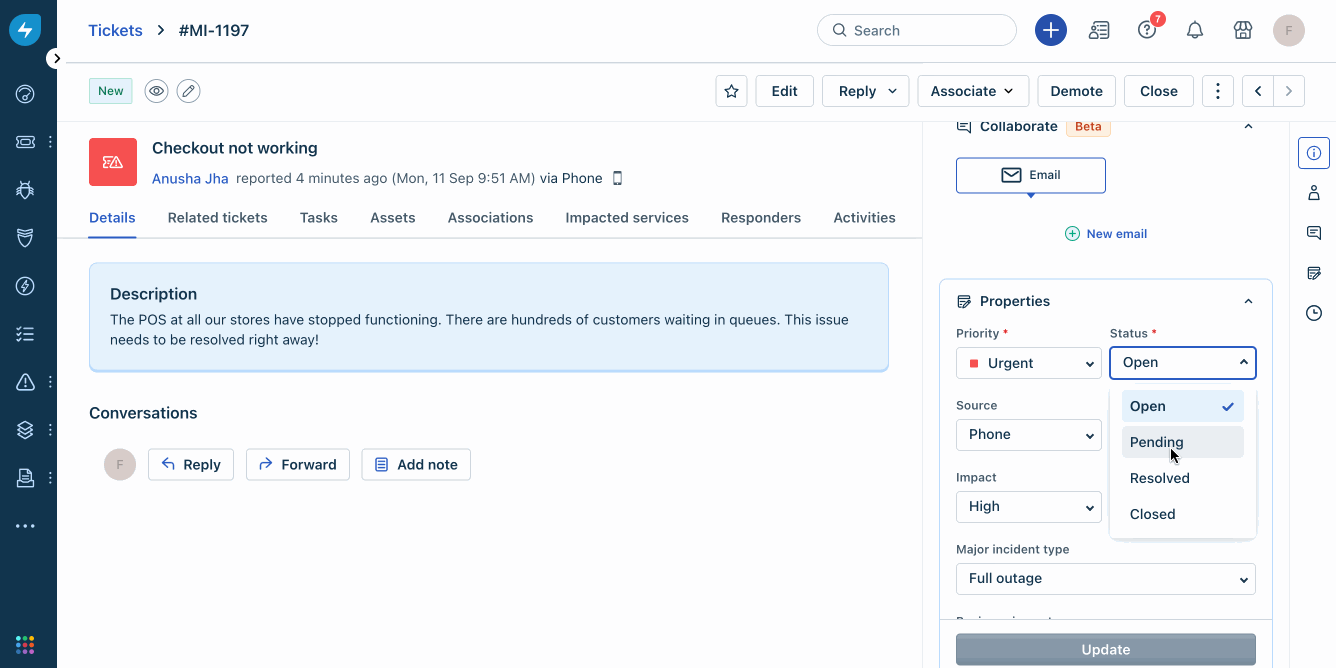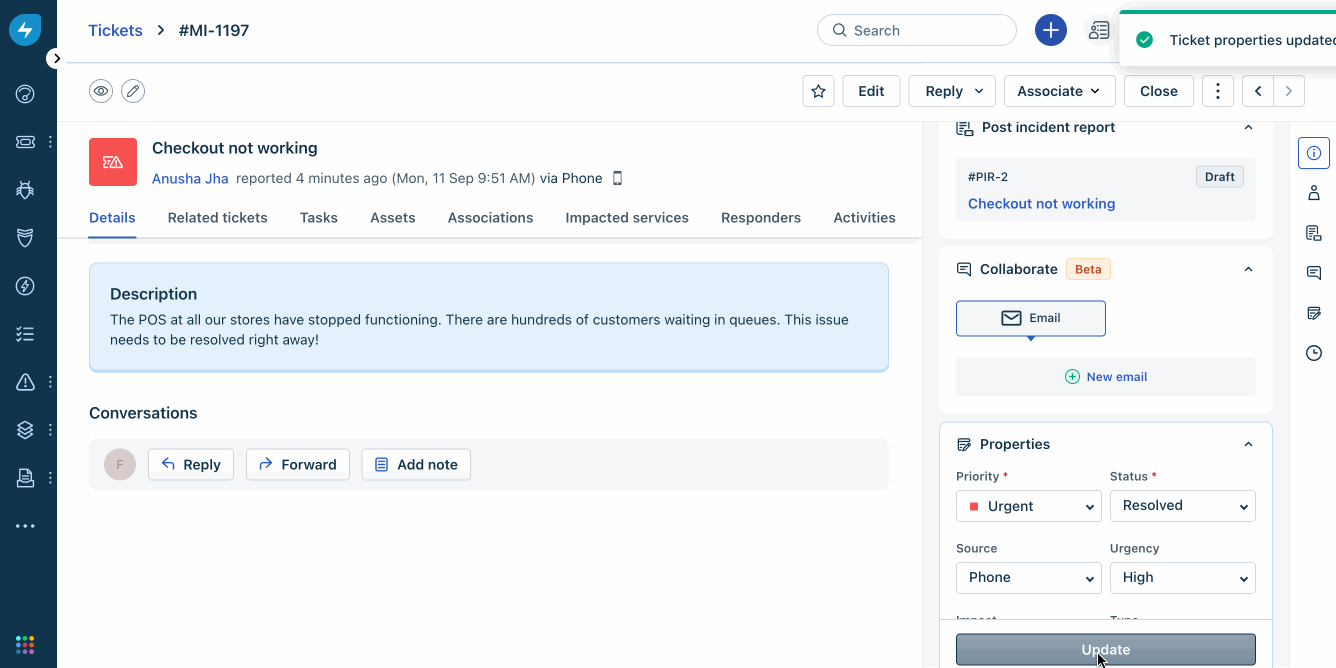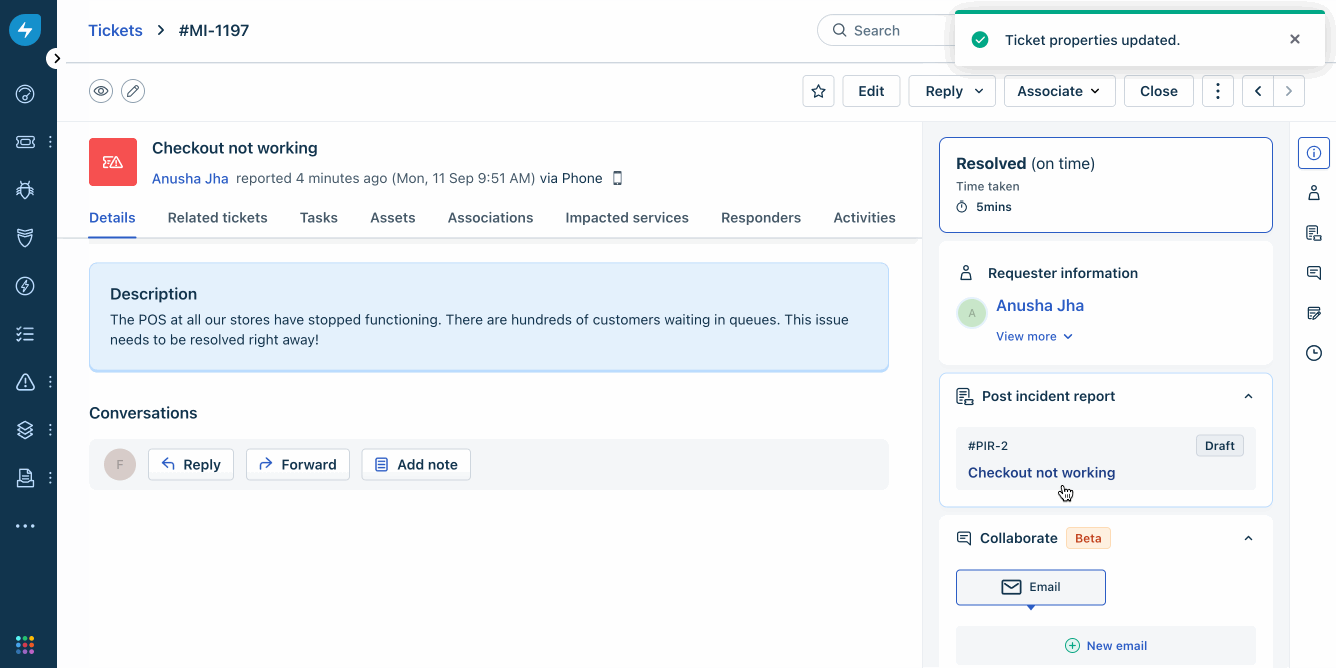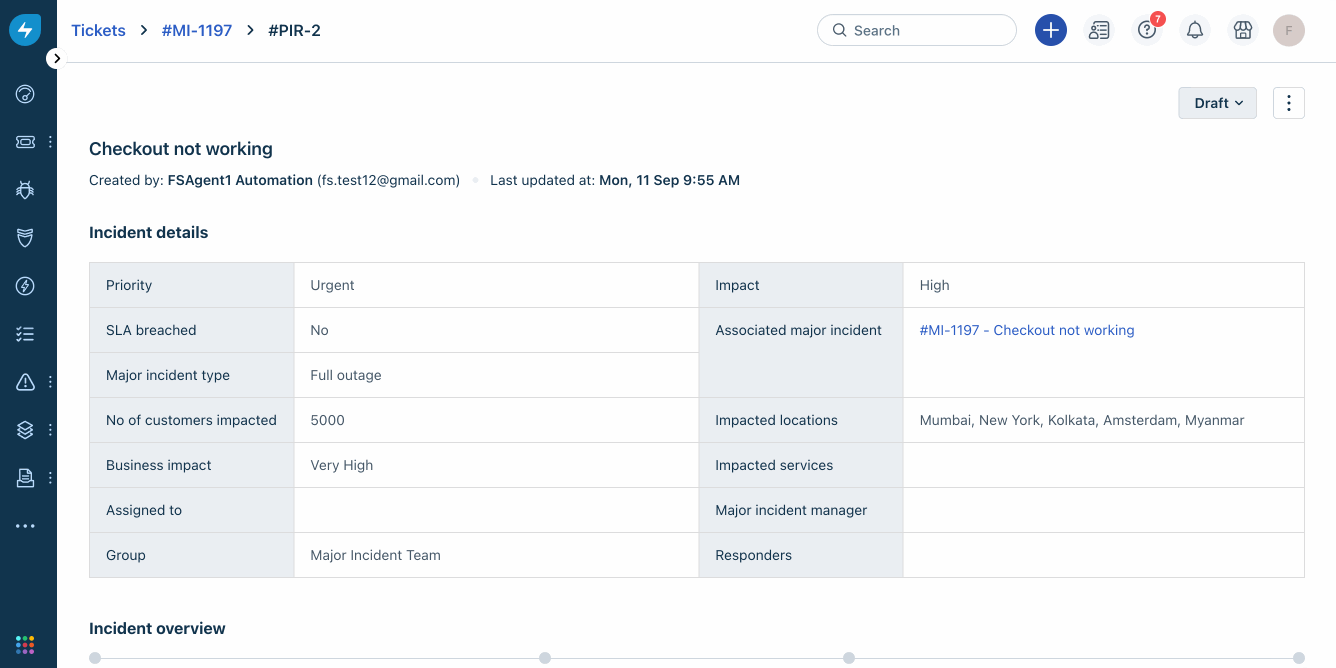
Source: Freshservice
Features that attract attention:
- Incident, problem, and change management
- Automated ticketing system
- AI-powered suggestions for faster resolutions
- Self-service portal and knowledge base
- Integration with multiple third-party apps
ServiceNow
ServiceNow offers a comprehensive ITSM suite designed to consolidate IT services and tools. It features Now Platform, an AI-powered platform designed to automate processes and streamline workflows. It integrates with other apps to solve problems, allowing you to unite various functionalities on a single platform.
The cloud-based platform scales and adapts to your changing needs as your business grows. It also offers real-time analytics to help you measure your teams’ performance and ensure you’re meeting your goals.
Source: ServiceNow
Features that attract attention:
- Automated workflows for incident management
- Integration with other IT and business systems
- Real-time dashboards and analytics
- Mobile accessibility
- AI and machine learning capabilities for predictive analysis
Ivanti Service Manager
Ivanti Service Manager streamlines your workflows, automating processes to accelerate resolutions. It adapts to your business needs, allowing you to scale your service as needed. You can easily tweak its drag-and-drop interface, integrate assets and tools into one place, and monitor performance metrics with its role-based dashboards.
Source: Ivanti Community
Features that attract attention:
- Incident and problem management
- Change and release management
- Configuration management database (CMDB)
- Automation and workflow customization
- Self-service portal
ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus
ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus offers an enterprise service desk that unites IT and business capabilities. It offers a centralized view of your entire IT infrastructure, allows the integration of your incident management tools in one place, and enables the customization of your workflows and self-service portal. It comes with an advanced analytics suite that provides visual reports of your service desk performance, allowing you to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Source: ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus
Features that attract attention:
- Incident and problem management
- Change and release management
- Asset management and CMDB
- Automated workflows and ticketing
- Real-time dashboards and reports
SolarWinds Service Desk
SolarWinds Service Desk is a cloud-based ITSM platform designed to speed up the resolution of incidents with AI-powered tools. Its intuitive interface makes it easy to use. It automatically classifies and routes tickets while offering an assistive knowledge base to empower end users to help themselves. Customizable reports provide insights into your performance, allowing you to assess whether you’re meeting customer expectations and service-level agreements.
Source: SolarWinds Service Desk
Features that attract attention
:
- Incident and problem management
- Change management and release management
- Service catalog and self-service portal
- Asset management and integrated CMDB
- Automated workflows and ticketing
- Advanced reporting and analytics
SysAid
SysAid is an AI-powered help desk platform that integrates ITSM management, self-service options, and asset management. It accelerates resolution speeds with automated processes and customized workflows. You gain access to detailed reporting and analytics that enable smart decision-making.
Source: SysAid
Features that attract attention:
- Incident, problem, and change management
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- Self-service portal and knowledge base
- Integration with various IT and business systems
- Advanced reporting and analytics
Spiceworks Help Desk
Spiceworks offers a free IT help desk solution designed for small to mid-sized businesses. It provides essential tools for managing IT services and support, with an intuitive interface that simplifies ticketing and incident management. Spiceworks also offers a community forum and a wealth of resources for IT professionals.
Source: Spiceworks
Features that attract attention:
- Incident management and ticketing
- Customizable workflows
- Integration with network management tools
- Self-service portal
- Reporting and analytics
Cherwell Service Management
Cherwell Service Management is a comprehensive IT service management solution designed to help organizations improve service delivery and operational efficiency. It supports ITIL best practices and offers extensive customization options to meet unique business needs. Cherwell's codeless configuration capabilities allow users to easily adapt and extend the platform without needing advanced programming skills.
Source: Cherwell Service Management
Features that attract attention:
- Incident and problem management
- Change management and configuration management
- Customizable workflows and automation
- Self-service and knowledge management
- Real-time reporting and dashboards
To choose the best software for incident management, assess your business needs and match them with what the various ITSM desks have to offer.
Conclusion
Effective incident management processes can help you prevent future disruptions, improve your operational efficiency, save valuable time, and bolster security. But you can’t just wing it. You need exhaustive planning and testing. And you need to equip your teams with an ITSM tool that allows your teams to run all the incident management best practices in one place, from routing tickets to sending out alerts.
If you feel your ITSM system falls short of its task, we can help you transfer to a better one. Help Desk Migration offers an automated and secure platform that can make data migration fast and easy. Get a free demo here.
FAQs
A successful incident management process includes proactive detection, precise categorization, rapid prioritization, investigation, resolution, and post-incident review. Incident types—minor issues, service disruptions, or full-blown incidents—are classified to help the team address them appropriately.
With well-defined incident statuses (like “open,” “in progress,” and “resolved”), teams can manage cases through an incident management system efficiently. Maintaining a combination of incident logs and reports also strengthens incident analysis, helping teams meet service level agreement (SLA) targets, improve customer satisfaction, and minimize the overall impact of incidents on business operations.
Teams can identify incidents by monitoring various sources of incidents, including system alerts, user reports, and automated detection tools. Accurate categorization is essential, as it helps classify incidents by type, impact, urgency, and affected services. With a framework for incidents, the team can categorize each case consistently and manage them effectively through the incident management systems.
To create an incident management plan, start with a template that outlines crucial steps, roles, communication protocols, and escalation paths. Include predefined incident statuses and service level agreements so each team member knows their responsibilities.
Defining actions for each incident type—from low-impact issues to full-blown incidents—enables a consistent, efficient approach that ensures customer satisfaction and reduces downtime.
To achieve timely detection and reporting:
- Set up real-time monitoring and alerts for various incident types.
- Establish clear reporting channels for all employees.
- Train the team to recognize incidents early and respond quickly.
- With these practices in place, you minimize delays, reduce the impact of incidents, and improve SLA compliance.
Prioritize incidents by assessing both impact and urgency. Some helpful methods include:
- Using a priority matrix or framework for incidents to rank them
- Assigning statuses in the incident management systems to track progression
This approach ensures that critical, high-impact issues are handled first, helping the team meet SLAs.
Continuous improvement begins with post-incident analysis. Reviewing incident logs after resolving incidents allows your team to identify patterns, causes, and areas for improvement. By refining your incident management plan template based on these insights, your team can enhance its response strategies, maintain high service quality, and support a proactive incident management process.
Effective incident management requires alignment with related ITSM processes, such as change and problem management. Integrating incident data with these processes ensures insights from incident logs can help prevent future occurrences. For instance, by linking incidents to recent system changes, your team can improve the root cause analysis and streamline responses across the IT service landscape.
Automation in incident management accelerates response time and reduces manual workload:
- Automated ticket creation and classification help respond faster to common issues.
- Automated incident statuses streamline escalation paths and resolution steps.
- Routine task automation frees the team for more complex incidents.
Incorporating automation ensures efficiency, consistency, and a faster overall incident resolution process.
Throughout the incident management process, data privacy and security are paramount. Limit access to incident data to authorized users and follow best practices in data handling and storage to prevent breaches. An incident management system should support these standards by enforcing permissions and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, which in turn reinforces customer trust and mitigates risk.
Frameworks like ITIL and NIST offer structured guidelines for handling incidents efficiently. The benefits of implementing these frameworks include:
- Consistent processes that align with industry best practices
- Clear guidelines for responding to various types of incidents
- Increased organizational resilience through structured response standards
Adopting these frameworks supports a standardized, reliable approach that enhances service quality and maintains compliance with best practices in incident management.



