Running a busy call center can feel like running an on-call fire service, with support agents constantly racing to address the latest incoming issues.
Still, how much of the race is necessary?
The answer lies in measuring call center productivity. Taking a step back and setting the right metrics for your team reveals how well you're doing and where you can invest in doing better.
TL;DR: Increase Call Center Productivity with These Key Metrics
Call center productivity measures how efficiently resources—time, labor, and technology—assist customers. Two key factors drive it:
- Agent Motivation (Human Factor): Motivated agents take the initiative, suggest improvements, and own their work, while unmotivated ones do the bare minimum.
- Tools and Environment (Technology Factor): Reliable software boosts productivity, while frequent tech issues slow agents down.
Calculating call center productivity involves the formula: (Total Output / Total Input) * 100. However, deeper insights require tracking key performance indicators (KPIs).
What to measure: Top 10 call center metrics
- Average Call Duration – Measures the typical length of calls.
- Average Handle Time – Tracks time spent on customer interactions, including post-call work.
- First-Call Resolution Rate – Percentage of issues resolved in the first call.
- Call Abandonment Rate – Percentage of unanswered calls.
- Number of Agents per Hour per Call – Helps determine staffing needs.
- Average Wait Time – The time customers spend on hold.
- Service Level – Percentage of calls answered within a set time frame.
- Conversation to Close Rate – A success rate of closing sales.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSS) – Customer feedback on service.
- Volume and Quality of Work – Measure the quantity and quality of calls handled.
How to boost call center productivity:
- Pleasant work environment: Promote agent well-being through work-life balance, communication, and recognition.
- Training programs: Prepare agents for peak times and challenging calls with ongoing training.
- Leverage AI and automation: Reduce manual tasks, improve call routing, and speed up issue resolution with AI tools.
- Self-service options: Offer FAQs or knowledge bases to lower call volume and let agents focus on complex tasks.
- Integrate systems: Seamless software integration helps agents access customer data quickly, boosting efficiency.
- Use call center software: Call center software masters omnichannel customer service, consolidates requests into a single system, and relieves teams of manual tasks.
Enhancing these areas leads to happier agents, faster resolution times, and a more efficient call center overall.
What Is Call Center Productivity?
Call center productivity is a measure that shows how efficiently your call center uses resources such as time, labor, and technology to assist customers. Call center productivity is a direct result of agent productivity, which in turn depends on two things:
- Agent motivation (the human factor): An unmotivated employee will only perform their job mechanically and do the minimum. In contrast, motivated call center agents will be proactive in making suggestions to improve processes and also willing to admit their mistakes.
- Tools and environment (the technology factor): Constant hang-ups in call center software don’t contribute to agent productivity either. In fact, technology is one of the biggest factors that can hinder or boost call center productivity (more on this later).
How Do You Calculate Call Center Productivity?
When it comes to calculating call center productivity, a simple formula is
(Total Output / Total Input) * 100
where total output is the time agents spend serving customers or doing related work, and total input is the total number of hours worked.
This formula works well for getting a quick snapshot of your performance but not for digging deeper. To get a more detailed picture, you need to set up the right customer service metrics.
Ten Best Call Center Productivity Metrics to Measure
Getting a handle on your productivity makes sense, but what KPIs should you measure?
The best customer service metrics are ones that help you easily identify your call center's weak points—for example, by comparing the exact number of agents per hour per call and the average wait time. Call center metrics can also show how satisfied customers are with your customer service. Finally, you must also track agent performance metrics to get a complete picture of your call center performance.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Average Call Duration | Total billable duration of all calls / Total number of calls | 6-8 minutes |
| Average Handle Time | Total handle time (call duration + post-call work) / Number of calls | 8-10 minutes |
| First-Call Resolution Rate | (Number of requests resolved on a first call / Total number of calls) * 100 | 70-75% |
| Percentage of Unattended Calls (Call Abandonment Rate) | (Number of unanswered calls / Total number of incoming calls) * 100 | 5-8% |
| Number of Agents per Hour per Call | Total number of agents on duty / Total number of calls received during that hour | 2-3 agents per 100 calls |
| Average Wait Time | Total wait time / Number of calls | 30-60 seconds |
| Service Level | (Calls answered within target time / Total number of calls) * 100 | 80% in 20 seconds |
| Conversation to Close Rate | (Number of successful closes / Total number of conversations) * 100 | 20-30% |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSS) | Average score from customer feedback surveys (1-5 scale) | 4.0-4.5 (on a 5-point scale) |
| Volume and Quality of Work | Measures both the number of calls handled and the quality of interactions | Volume: 20-30 tickets/hour; Quality: 70-75% FCR, 4.0-4.5 CSS |
Here are ten simple metrics to get you started.
1. Average call duration
Average call duration (ACD) measures how long calls take on average. It’s calculated by dividing the total billable duration of all calls by the total number of calls. ACD can be useful for identifying patterns or trends, such as peak times or common reasons for long calls. This support agent performance metric also lets you calculate average handle time.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Average Call Duration | Total billable duration of all calls / Total number of calls |
|
2. Average handle time
Average handle time (AHT) measures support rep productivity in terms of the time they spend handling customer interactions, including call duration and post-call work. You can use AHT to determine staffing and resource needs such as training, process changes, or software updates.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Average Handle Time | Total handle time (call duration + post-call work) / Number of calls |
|
3. First-call resolution rate
The first-call resolution rate (FCR) is the percentage of customer requests resolved during the first call. It’s calculated by dividing the number of requests resolved on the first call by the total number of calls.
A high FCR shows that your customers are resolving their issues efficiently without calling back multiple times. This is one of the best customer service metrics, as customers are naturally happier if their issues get resolved in one call.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| First-Call Resolution Rate | (Number of requests resolved on a first call / Total number of calls) * 100 |
|
4. Percentage of unattended calls (call abandonment rate)
The percentage of unattended calls, aka the call abandonment rate, is the percentage of calls your agents don’t answer. It’s calculated by dividing the number of unanswered calls by the total number of calls.
A high abandonment rate means that a significant number of customers hang up before their call is answered, which may indicate poor call routing, inadequate staffing, or long wait times.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Percentage of Unattended Calls (Call Abandonment Rate) | (Number of unanswered calls / Total number of incoming calls) * 100 |
|
5. Number of agents per hour per call
If your call abandonment rate is high, you may want to look at another metric: the number of agents per hour per call. This metric shows how many agents are available to handle calls in a given time period. To calculate the number of agents per hour per call, divide the total number of agents on duty during a given hour by the total number of calls received during that hour.
This call center metric helps you determine the number of agents needed to handle call volume at different hours of the day—especially at peak times—to achieve optimal customer service staffing.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Number of Agents per Hour per Call | Total number of agents on duty / Total number of calls received during that hour |
|
6. Average wait time
If your call center agents fall short or simply aren't enough to handle the call volume, expect a high average wait time. As the name implies, this KPI refers to the average time a customer spends on hold before being connected to a customer service representative.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Average Wait Time | Total wait time / Number of calls |
|
7. Service Level
Call center service level is typically calculated as the percentage of calls answered within a specified time—such as within 20 or 30 seconds—in relation to the total number of inbound calls. A standard service level is often set by an industry or a particular company. A low service level metric may indicate understaffing or problems with call routing and management.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Service Level | (Calls answered within target time / Total number of calls) * 100 |
|
8. Conversation to close rate
This is one of the outbound call center metrics that measure agent productivity in closing sales during the last customer interaction. This metric is calculated by dividing the number of successful closes or desired outcomes by a target number of successful outcomes. You can use this KPI to measure the performance of either a specific agent or an entire sales team.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Conversation to Close Rate | (Number of successful closes / Total number of conversations) * 100 |
|
9. Customer satisfaction score
Unlike some of the earlier call center metrics, the customer satisfaction score (CSS) focuses entirely on customer experience and shows how satisfied customers are with the service they receive. A low CSS may indicate low agent productivity and vice versa.
A CSS is typically calculated through a survey of customers who have recently interacted with customer service. In the survey, customers are asked to rate their satisfaction on a scale of 1 to 5 or with phrases such as "very satisfied," "satisfied," "neutral," "dissatisfied," or "very dissatisfied." The survey results are then used to calculate an overall CSS.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSS) | Average score from customer feedback surveys (1-5 scale) |
|
10. Volume and quality of work
Volume and quality of work metrics help evaluate the amount and quality of work an agent or team performs.
- Volume of work indicates how many calls or interactions an agent or customer support team handles. It can include average handle time, service level, and abandoned call rate.
- Quality of work measures agent productivity in terms of the quality of interactions between reps and customers. It can include agent performance metrics such as first-call resolution, conversion to close rate, and customer satisfaction score.
Together, volume and quality of work metrics give you an overall view of customer support team performance and help you identify high- and under-performing support reps and teams.
| Metric | Formula | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Volume of work | Number of tickets handled per agent per hour. | Volume:
|
| Quality of work | First-call resolution rate, customer satisfaction score. | Quality:
|
Now that you know which agent performance metrics to measure, let's move on to the best tactics for increasing customer service productivity.
How to Increase Call Center Productivity?
As you’ve already seen, call center productivity is influenced by both people and technology. In our tips, we’ll examine both of these factors.
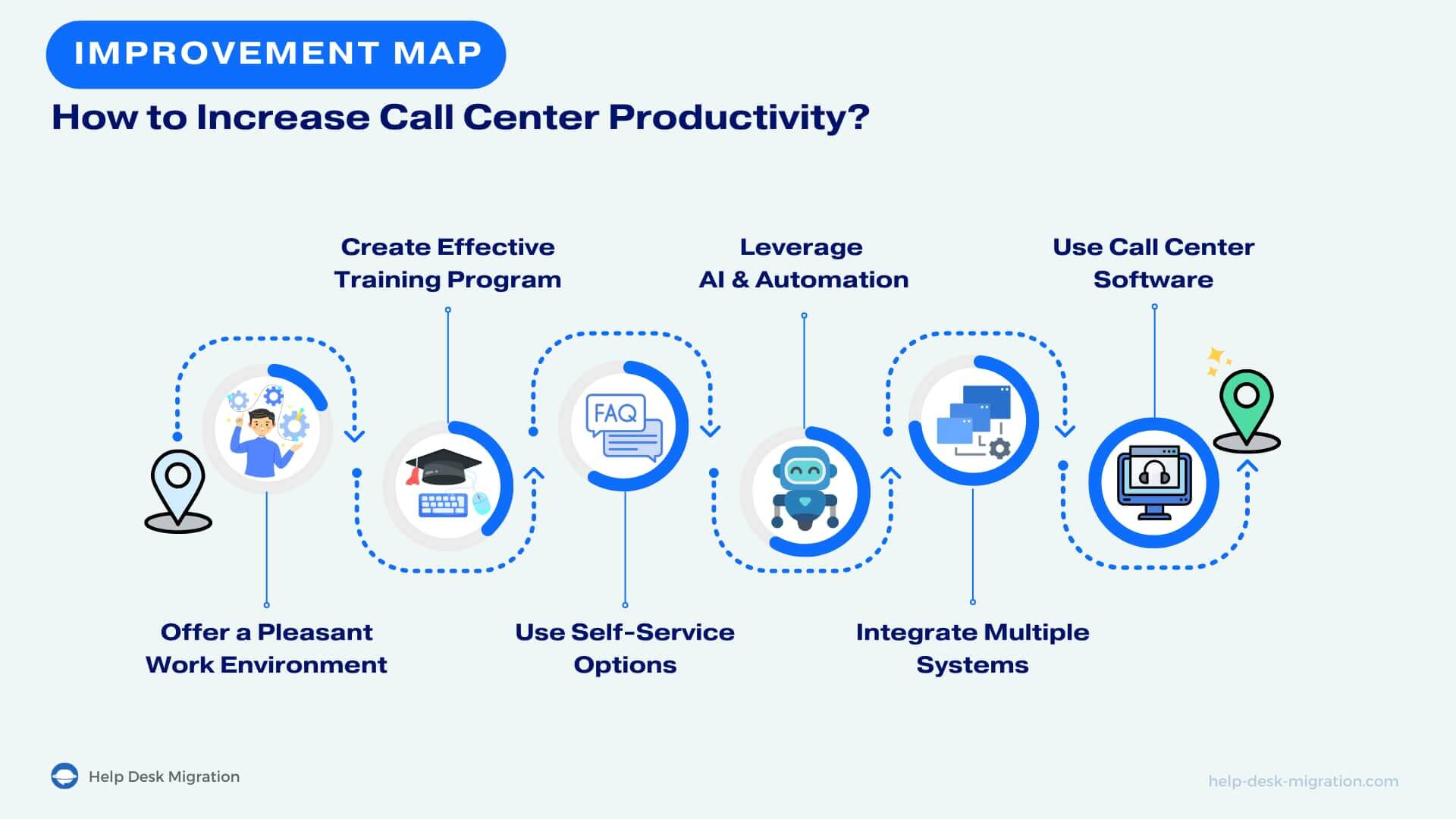
1. Provide a pleasant work environment
Research suggests that keeping workers happy can boost employee productivity by 12%. Here are some steps you can follow to reach or exceed this figure:
- Communicate effectively. Encourage open communication, set up regular 1:1 reviews, and provide regular feedback to employees. Make sure that agents feel heard and valued.
- Show appreciation. Recognize and reward agents for good work and contributions. Appreciation can boost morale and motivation.
- Set a good example. Be respectful, approachable, and supportive as a leader.
- Promote work-life balance. Allow employees to take time off when needed, and if possible, offer hybrid schedules.
A positive work environment will help you retain support agents and reduce the need for new hires who are less productive during training.
2. Create an effective training program
Training programs are necessary so your call center agents don't feel alone on challenging calls. You can start by discussing agent issues in detail and offering mentoring, especially during night shifts. It also won’t hurt to document action plans or best practices for specific cases. An internal knowledge base will give agents more confidence on the job.
But training isn’t just about agent experience. Well-trained and conscientious agents are more likely to improve all key call center metrics, including customer satisfaction, meaning your customers will spend less time on hold and call abandonment will go down.
Unfortunately, training can fall short if your overall environment doesn’t support the outcomes well. Using the latest technology can significantly boost the productivity of your team and your call center as a whole.
3. Deploy AI for automating manual tasks
AI has the potential to improve customer service significantly.
For example, AI-driven interactive voice response goes beyond traditional chatbots. This technology lets customers ask questions and get pre-defined answers or automatically directs them to a representative based on their query. As a result, customers reach the right agent and get the help they need on the first try, leading to fewer calls, shorter average wait times, and higher first-call resolution rates.
There are other applications, too. AI-powered systems can identify patterns and trends in historical call center data, such as transcripts and recordings. Call center managers can then use this information to make better data-driven decisions faster.
4. Use self-service to reduce call volume
Setting up self-service portals such as knowledge bases and FAQs can improve productivity in two main ways, even when your team isn’t available.
- Shorter customer wait times. Hubspot reports that in 90% of cases, customers prefer an immediate response to their issues. Self-service can often help customers resolve simple issues themselves without waiting on hold.
- Fewer agent interactions. 81% of all customers prefer to resolve their problems themselves before contacting a live operator. A self-service system lets customers get the information they need without speaking with a customer support team rep. As you reduce the need for human support agents, you can also reduce the cost of handling customer interactions across channels.
5. Integrate multiple systems for greater visibility and easy access
Call center agents typically work with a variety of applications, such as help desks or CRMs, live chats, desktop softphones and mobile apps, call conferencing, Interactive Voice Response (IVR), Automatic Call Distribution (ACD), and customer satisfaction surveys. When these services are poorly integrated, support agents must navigate multiple systems and average handling time increases. Linking different software systems and technologies helps create a seamless and efficient workflow.
Better integration helps consolidate requests from multiple resources into a single system. This allows call center agents to see all of a customer's interaction history at once and resolve issues without wasting time asking for previous information.
6. Use call center software
Software for call centers helps you master omnichannel customer service. This solution automates the receipt of requests and consolidates them into a single system.
But that's not all it can do. The main advantage of call center software lies in relieving teams of manual tasks. For example, it can provide managers with comprehensive statistics, such as average call handling and waiting time, call duration, and agent occupancy. This allows them to do the rest of their work more efficiently, which increases the call center's overall productivity.
Sum up
Most call centers are busy, but effective ones are busy with the right things. Measuring call center productivity gives you a starting point for improving agent performance, customer satisfaction, and overall call center efficiency.
Call Center Productivity FAQs
- Healthcare: Prioritizes urgent response times and compliance.
- Retail: Emphasizes quick resolutions and customer satisfaction.
- Finance: Focuses on accuracy and security.
Tailoring metrics to these industry needs ensures more relevant performance measurements.
- Provide comprehensive training to boost efficiency.
- Use advanced tools and AI to automate and streamline workflows.
- Monitor key performance indicators for insights.
- Encourage open communication and recognize achievements.
- Reduce call volume with self-service options.
- Monitor workloads: Use data to track call volumes and adjust staffing as needed.
- Distribute tasks evenly: Ensure tasks and calls are evenly distributed among agents.
- Support: Offer regular breaks, manage stress, and provide resources for help.
- Implement flexible scheduling: Provide flexible shifts to accommodate personal needs and prevent overwork.
Conversely, off-peak periods might result in lower call volumes, allowing for better workload management and more efficient operations. Adjusting staffing and resources to match these fluctuations is key to maintaining productivity and service quality.
- Offer greater flexibility and reduce overhead costs.
- May require additional effort to ensure effective team communication and collaboration.
- Varying work environments can affect performance and productivity.
- Agents may face technical difficulties that impact their efficiency.



