What stands behind exceptional customer service? Is it great communication, helpful support agents, and blazing-fast replies? Nope. A recent report states that 81% of clients expect companies to provide more self-service options as part of their customer service.
But exactly what does offering self-service mean? Self-service lets your customers access resources to find solutions on their own without requiring assistance from a representative. Sounds like a good plan, but to make it work, you need to do some homework.
Self-service lets your customers access resources to find solutions on their own without requiring assistance from a representative.
This guide shows you how to harness the power of self-service and the role of a knowledge base strategy to satisfy your customers’ needs. We’ll lead you through the features and advantages of knowledge bases, and the steps to create a self-service knowledge repository your customers and employees can benefit from.
Let’s start with the basics.
What Is a Knowledge Base?
A knowledge base (KB) is a centralized repository of how-to guides, instructions, and other helpful information. It lets your customers and employees easily find solutions to problems without contacting a support team.
Knowledge-base content typically covers:
- Standard operating procedures
- Answers to frequently asked questions
- Product or service usage guidelines
- Troubleshooting manuals
- Learning materials, training and tips
- Onboarding modules for new hires
The content will vary depending on a company’s specifics, its audience, and many other factors. Let’s take a closer look at these differences.
What Type of Knowledge Base Should You Choose?
Depending on your target user and the purpose of sharing information, a knowledge base can be internal or external.
What’s an internal knowledge base?
As the name suggests, an internal knowledge base is a private, within-company self-service repository of information about your business’s products, services, or procedures. It provides employees and company contractors with all the essential information they need to do their job.
Why do you need an internal knowledge base?
This type of knowledge base lets your team collaborate and share company knowledge internally. It can support multiple departments and allows you to set up roles and permissions to limit access to specific information.
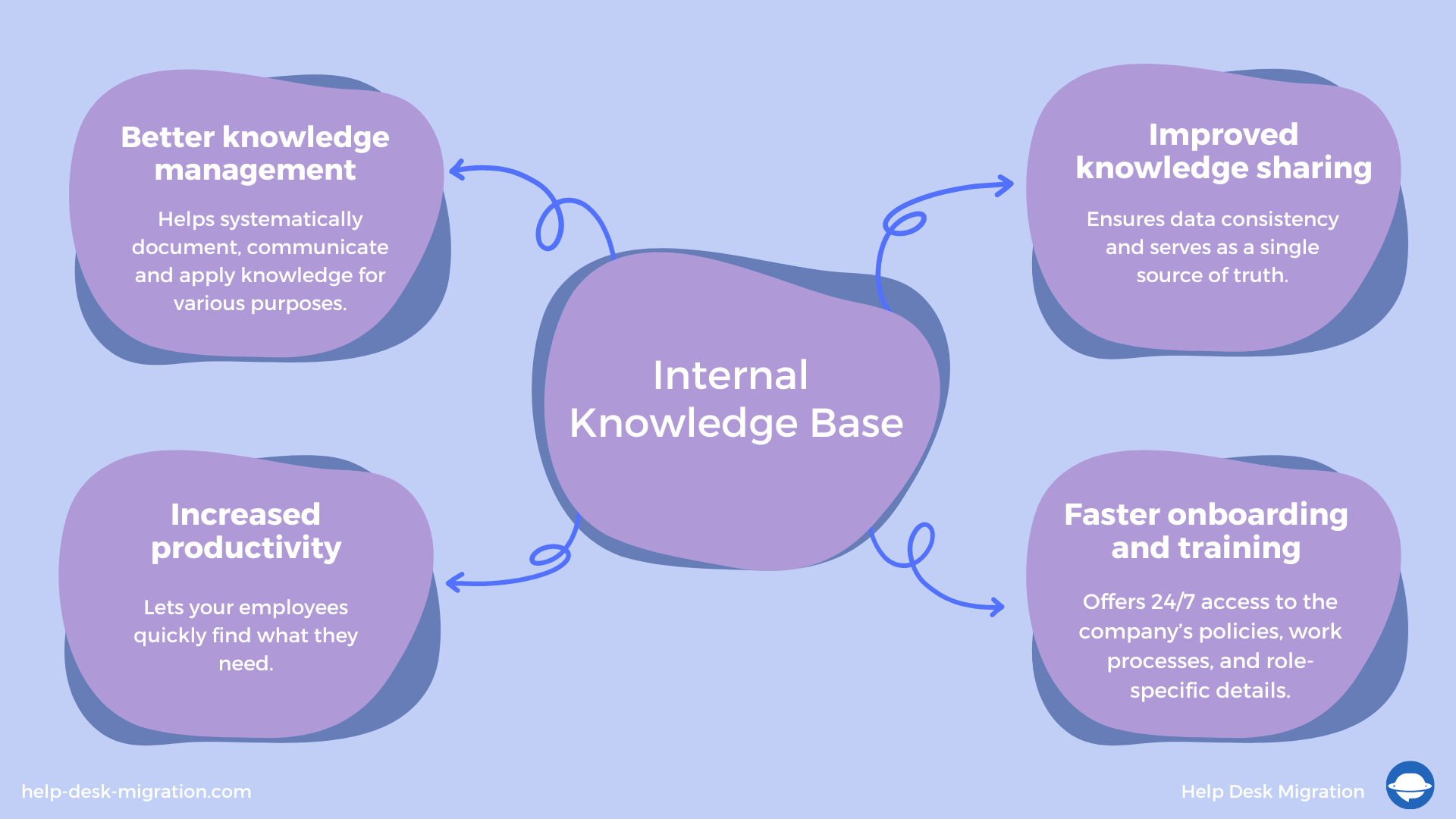
Here are some benefits an internal KB can offer:
- Better knowledge management. A knowledge base can help systematically document, store, communicate, and apply organizational knowledge for various purposes.
- Increased productivity. Knowledge management (KM) tools let your employees quickly find what they need—no more pestering colleagues with questions or digging through pages of emails and documents.
- Improved data sharing and knowledge transfer. KM tools provide data consistency and serve as a single source of truth. This ensures that all employees and departments instantly receive updates and remain on the same page.
- Faster onboarding and more efficient training. A centralized knowledge base offers your new hires 24/7 access to your company’s policies, work processes, and role-specific details. This makes the entire initiation process faster, smoother, and accessible remotely.
Since an internal KB usually contains proprietary company information, ensure the provider you choose guarantees data protection and robust access and permission-setting capabilities. But remember that data leakage is caused by the weakest link, which is definitely the humans who use the KB. So remember to review permissions, organize and secure your content wisely to protect your company's data.
What is an external knowledge base?
An external knowledge base aims to share information about a company’s products and services with its customers and provide them with 24/7 assistance. With 89% of millennials using a search engine to find answers before contacting customer service, an external knowledge base is a must to fulfill customer expectations.
But this type of knowledge base can offer you much more. Read on to discover more benefits of external KBs.
Why Does a SaaS Service Need an External Knowledge Base?
If you’re in the SaaS world, you know that excellent customer service can help you stand out, grow and retain your customer base. Studies show that if users find your customer service deficient, 59% of them will silently churn.
A knowledge base provides excellent opportunities to retain customers and introduce your service to potential new customers.
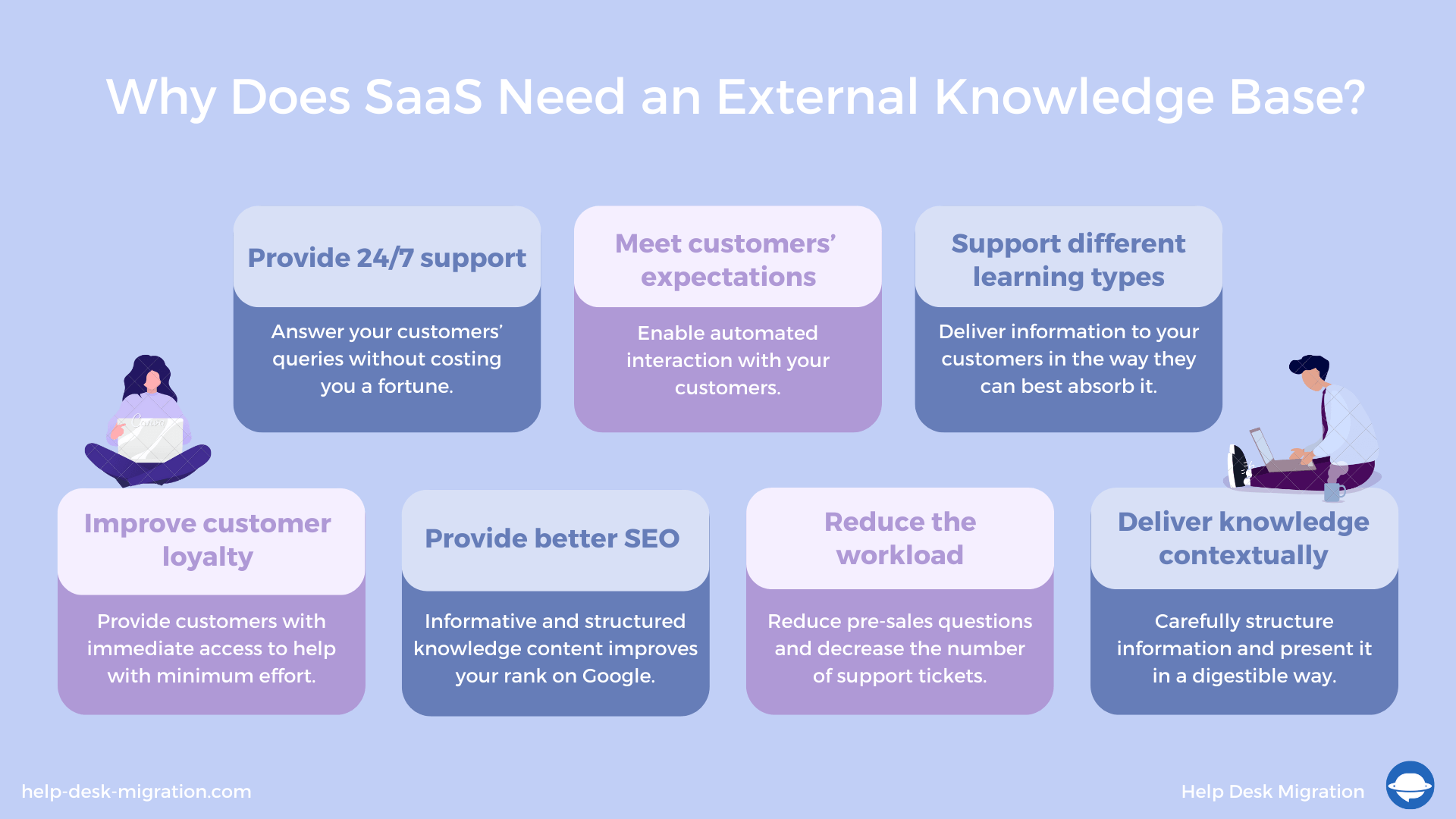
Provide 24/7 support
Zendesk's study found that 47% of customers expect businesses to provide round-the-clock support, yet only excellent customer service can help you stand out, grow and retain your customer base. 28% of customer support teams are available 24/7. An external knowledge base with a self-service portal can answer your customers’ queries without costing you a fortune.
Improve customer loyalty
95% of consumers believe customer service is the main factor impacting their brand loyalty decisions. Knowledge management tools offer customers immediate access to help with minimum effort on your part.
Provide better search engine optimization
Informative and properly structured knowledge-base content improves your company’s rank on Google. Pillar pages, topic clusters, and hyperlinking make your content more digestible and streamlines service for your customers. The more people engage with your content, the higher it ranks on Google and attracts new customers.
Meet customers’ self-service expectations
Today’s consumers have become accustomed to using automation like bots and other intelligent tools to address their issues. Creating an external knowledge base helps foster automated interaction with your customers. A whopping 78% of business leaders in the US already invest in self-service to deliver proactive customer care.
Reduce the load on your customer support agents
Harnessing the power of self-service can reduce pre-sales questions and decrease the number of support tickets by 56%. And when your customer support agents have fewer tickets to deal with, they can respond to those more quickly.
Support different learning types
Unlike traditional customer service, a knowledge base can offer information in plain text, as graphical instructions, video tutorials, audio guides, and other accessible formats. This helps cover almost all types of learners’ needs, so you can deliver information to your customers in the way they can best absorb it.
Deliver knowledge contextually
Self-service capabilities let your customers quickly get the information they need and quickly find solutions. No need to look through hundred-page manuals. Knowledge-management tools let you carefully structure information and present it in a digestible way.
If all those perks sound tempting, let’s see how you can build your own KB.
How to Build a Knowledge Base?
In the 2020’s, you don’t need to reinvent the wheel and develop a knowledge management tool from scratch. The market is replete with options for all needs and budgets. In the next section, we list the most popular types of KBs to help begin putting your knowledge base strategy in motion.
Help desk software module
Help desk solutions often come bundled with knowledge base software. No surprise, as they both serve to help resolve customer support queries. The difference is that the help desk is used by support agents to handle tickets, while the knowledge base serves as a read-, watch-, or listen-only portal for customers (or internal users) to search for answers on their own. Good examples of knowledge-base software are Zendesk and Intercom Articles.
Knowledge management solutions
These IT systems store and retrieve the company’s knowledge and help improve understanding, collaboration, and process alignment. Knowledge management systems can exist within organizations offering safe space for collaboration. But they can also serve to center your knowledge base for your users or customers. Tools like Atlassian’s Confluence or HelpCrunch are good examples of such foundations for building your knowledge base.
Standalone knowledge base software
Standalone KB software is a specialized tool for creating, maintaining, and delivering self-service content to your customers. For example, Document360 and Helpjuice offer myriad features and suggestions to create your knowledge base from scratch.
Now let’s look at the features to look for in a knowledge base software so you can make the right choice.
What Features Should Knowledge Base Software Have?
Your knowledge base should be a one-stop shop where your team and customers can find the information they need. But it should also let your support team easily create, manage, and share content.
Here are the eight most essential features to look for when choosing a knowledge management tool.
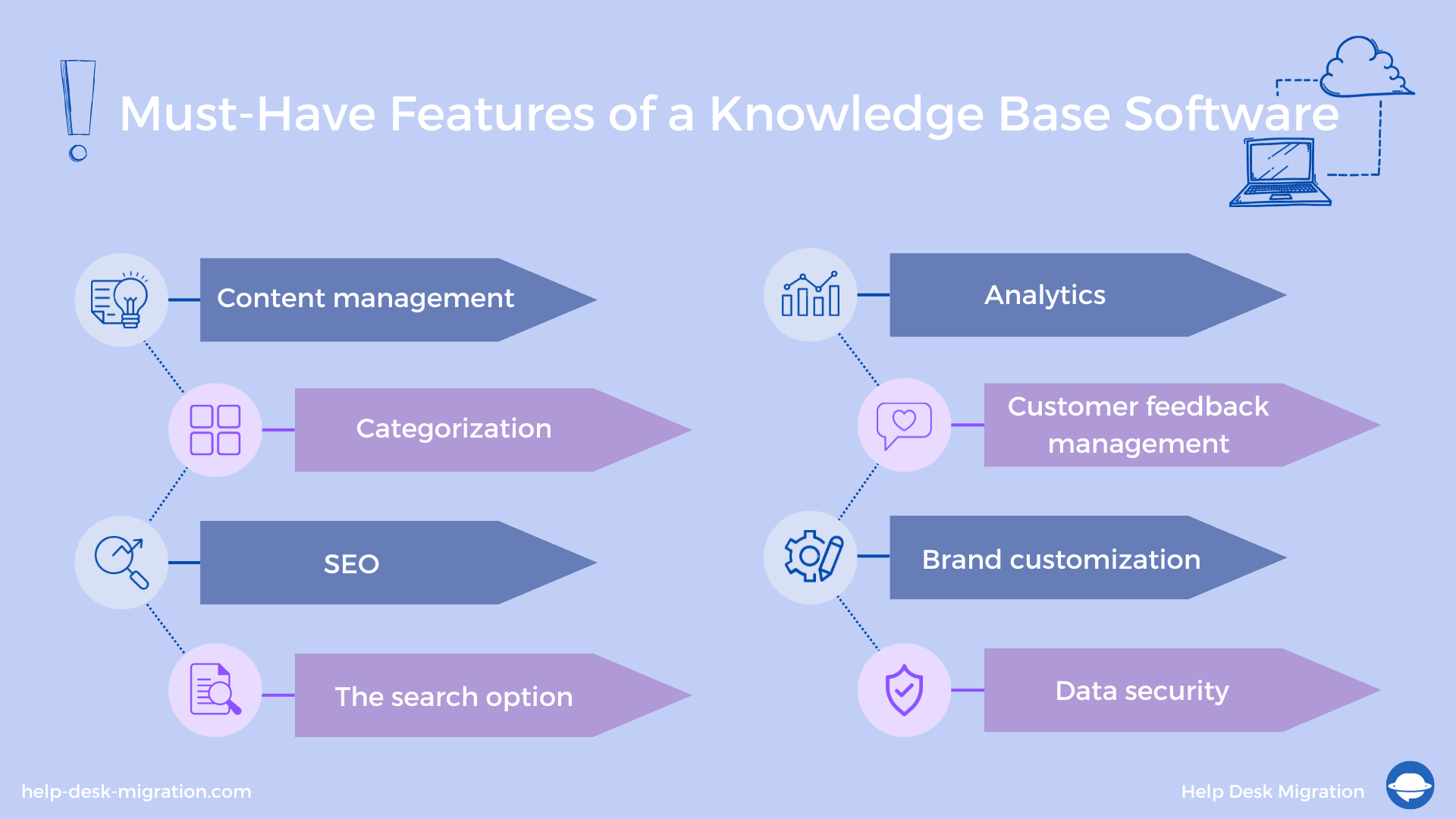
- Content management provides intuitive tools to create, update, schedule, and publish your company knowledge.
- Categorization helps create order out of chaos and lets you designate top-level categories, subcategories, and topic clusters so you can easily reorder and label content. Categorization lets you easily find any information you need.
- SEO lets you increase your knowledge base’s ranking in popular search engines and drive organic traffic to your website. Knowledge management tools enhanced with SEO features allow you to manage on-page and technical SEO, suggest optimal keywords for search engines, and can even automatically generate titles for different pages.
- The search option lets your team or customers find and share information quickly. Most content management tools offer full-text search and filters to get people the information they need quickly.
- Analytics help you better understand end-user engagement with your knowledge base. For example, it lets you set up and check metrics, run statistics, and see the geography of your users.
- Customer feedback management helps you manage customer feedback and track likes and dislikes for each knowledge-base category and page.
- Brand customization aligns your knowledge base with your company’s identity. This means, for example, selecting colors, icons, and themes associated with your company, plus customized navigation and any necessary integrations.
- Data security is designed to protect data by setting roles, restrictions, permissions, and automatically scheduled backups.
Now that you know what features to look for in knowledge management tools, let’s discover how to fill it up right.
How to Create Knowledge Base Content?
Filling up your shiny new knowledge base with the right content requires more time and effort than simply installing software. Whether you already have some documentation or are just beginning to create it, this knowledge base guide will focus your efforts in the right direction.
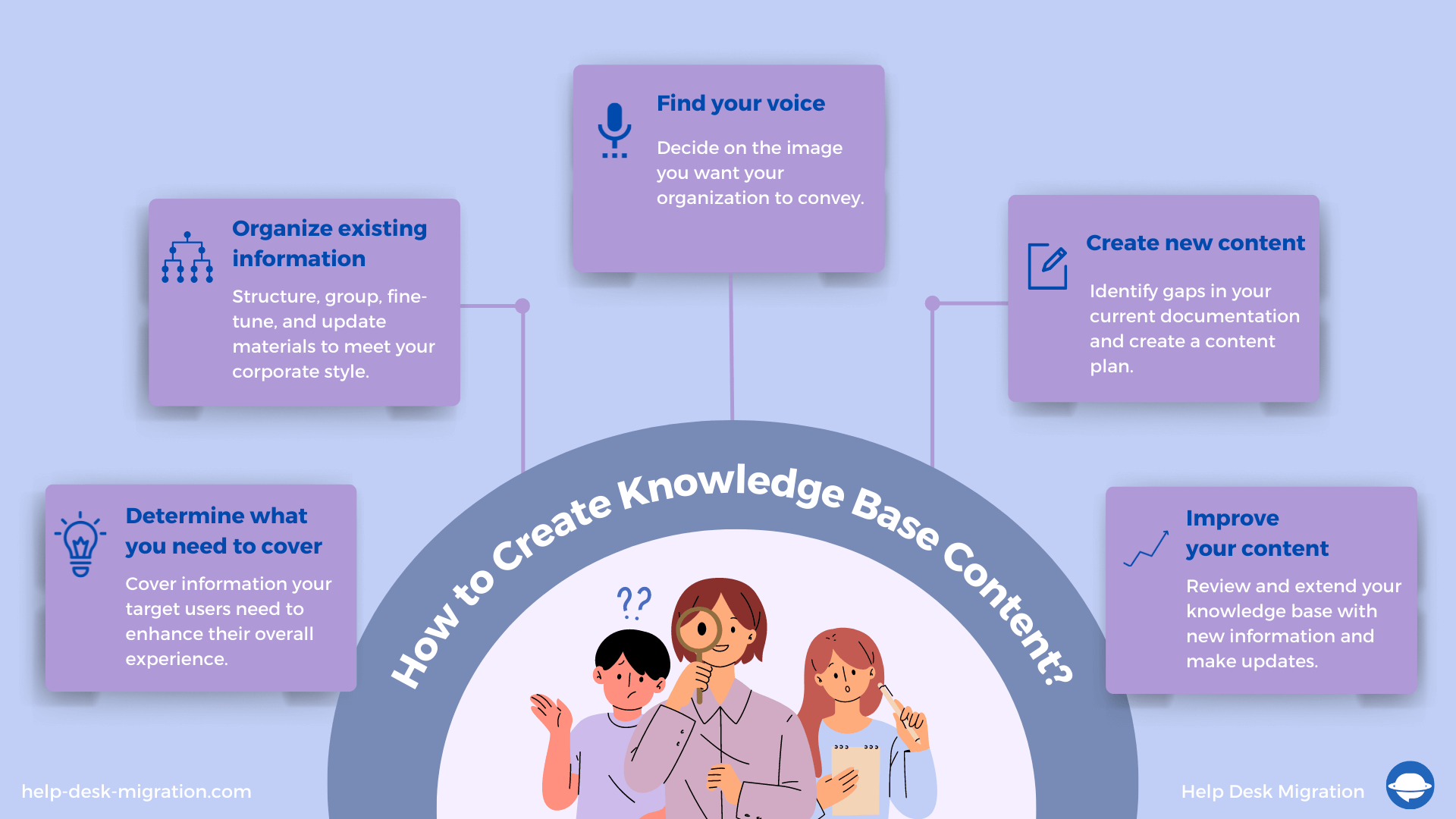
Step 1. Determine what you need to cover
Your knowledge base content should cover information your target users need to enhance their overall experience. This can include:
- Frequently asked questions. When a customer has a basic question about your product or service, they’ll likely visit the FAQ section first. Check with all your departments and document whatever frequently asked questions they receive (with answers of course).
- Introductory videos. Your customers (and team members) may struggle with your product or service setup process. An excellent way to solve this problem is to record basic “getting started” and onboarding video guides.
- Tutorials and walkthroughs. This section can guide your target users through routine and advanced features of your product or service.
- Community-powered forums. Forums let users communicate and exchange answers with each other. Your company should moderate the questions and answers users post and step in only when necessary.
- Updates and releases. Inform your users of new features or product versions and share guides so they can make the most of them.
- Documentation and reference articles. Engage with subject matter experts to explain the technical aspects of your products or services for customers and create engaging content that meets your audience’s needs.
Step 2. Collect and organize existing information
You likely already have many guides and tutorials hidden in emails or shared documents. All you need is to structure, group, fine-tune, and update those materials to meet your corporate style.
Step 3. Find your voice
Decide on the image you want your organization to convey: formal, friendly, unbiased, or maybe laid-back. Then establish style guidelines and follow them throughout your knowledge base. This brings consistency and a branded feel to your published information. Marketing professionals can help you find your voice.
Step 4. Create new content
Identify gaps in your current documentation and create a content plan that lists questions you need to cover on different topics. Everyone on your team and even your customers can help you generate new content, but make sure subject matter experts review it before publishing.
Step 5. Improve your content
Your knowledge base is not a thesis you write and put on a shelf. It should reflect even the slightest changes to your product or service. Assign a person or a team to constantly review and extend your knowledge base with new information, make updates, and delete outdated articles.
Knowledge management is a constant task that requires repeatedly completing all these steps. If you do it right, you’ll have many opportunities to beat the competition.
Summing up
A well-structured knowledge base can save you enormous amounts of time and money, and make your customers and internal team happier. It provides convenient access to information, which lets you streamline customer service and help employees perform more efficiently.
An internal KB can help you boost productivity, foster collaboration and data sharing, and easily onboard new team members. An external KB supplements your customer support team and satisfies consumers’ desire to self-serve. It reduces your support costs, improves customer loyalty, and draws in new customers.
Various tools can help you build a knowledge base. But if you make the wrong choice—don’t worry. You can still migrate to a tool with better knowledge management capabilities. Help Desk Migration has your back. We’ll help you effortlessly move all the documentation and language translations you painstakingly created to a new platform.


